The physiologist J. Soum surgically sealed off an air sac of a pigeon and injected carbon monoxide into it. What did he observe and conclude from this experiment?
A. The bird died demonstrating the toxicity of this gas.
B. The bird was fine, demonstrating this gas is not actually toxic.
C. The bird died, indicating diffusion of gases across the air sac into the blood.
D. The bird showed no ill effects, indicating diffusion of gases from the air sac into the blood.
E. The bird showed no ill effects, indicating gases do not diffuse from the air sac into the blood.
E. The bird showed no ill effects, indicating gases do not diffuse from the air sac into the blood.
You might also like to view...
Explain why only anaerobic bacteria inhabited Earth for the first two billion years of its existence
What will be an ideal response?
What nucleotide change is a shared derived character for species A, B, and C, but not for species G?
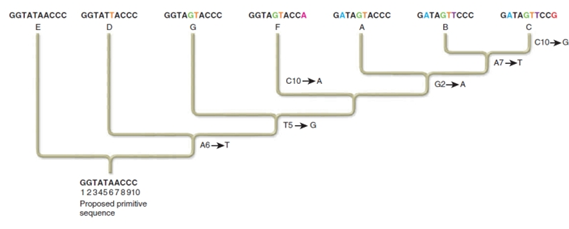
A,T,G, and C refer to nucleotide bases, and the numbers refer to the position of the base in the nucleotide sequences.
For example, A6 refers to an adenine at the sixth position.
A. Changing the second G to an A is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
B. Changing the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
C. Changing the second G to a T is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
D. Changing the second G to an A and the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
E. None of these show a change in derived characteristics for A, B, and C that are not found in G.
Which of the following is not a reason why Neurospora is an ideal organism to study the effects of
genetic mutations? a. Neurospora is easy to grow. b. Neurospora grows as a haploid organism. c. Neurospora manufactures all its necessary molecules when grown on a minimal medium. d. A mutant Neurospora strain that cannot make a particular amino acid can still grow if that amino acid is added to the growth medium. e. Neurospora contains homologous chromosomes that are easily viewed with a light microscope
What is the name of the tube through which urine leaves the urinary bladder?
a. renal vein b. collecting duct c. urethra d. renal pelvis