Carol sees a light bulb turn red, then turn blue. If you are moving near the speed of light past Carol, what do you observe?
A) You also see the light bulb turn red, then blue.
B) You observe the light bulb turn blue first, then red.
C) You observe the light bulb turn red and blue at the same time.
D) What you observe depends on how fast you are moving.
A) You also see the light bulb turn red, then blue.
You might also like to view...
The figures below represent interference fringes. The distances from the screen to the slits is the same for each figure, and the planes of the screen and the slits are parallel. Which figure(s) represent(s) slits with the greatest spacing d between the slits? The white spaces represent the interference maxima
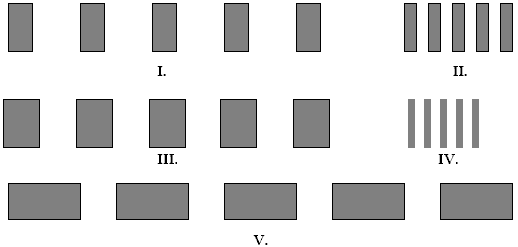
a.
I.
b.
II.
c.
III.
d.
IV.
e.
V.
Radiation: Two identical objects are placed in a room with a temperature of 20°C. Object A has a temperature of 50°C, while object B has a temperature of 90°C. What is the ratio of the net power emitted by object B to the power emitted by object A?
A. 1.7 B. 2.8 C. 81 D. 17 E. 21
Einstein's general theory of relativity suggests that gravity is
A) a force of attraction that acts at a distance between two masses. B) caused by curvature of spacetime. C) = G × M1 × M2/d2. D) one of four fundamental forces in nature.
One experimental observation that demonstrates Einstein's ideas on the relativity of time, is
A) electromagnetic waves from the early stages of the development of the universe have slower rates of vibration. B) muons "live" longer when moving rapidly than they do when they are at rest. C) a laser beam emitted from an orbiting satellite is observed from Earth. D) rapidly-rotating neutron stars spin more slowly than they would if they weren't moving rapidly away from us. E) the recent discovery of very fast-moving particles known as tachyons.