Suppose a person's utility for leisure (L) and consumption (Y) can be expressed as U = Y ? L and this person has no non-labor income. Assuming a wage rate of $10 per hour, show what happens to the person's labor supply when the person wins a lottery prize of $100 per day
What will be an ideal response?
Rearranging yields U = (Y* + 10H) ? (24 - H) = 24Y* + 240H - Y*H – 10H^2. Maximizing utility with respect to H yields dU/dH = 240 - Y* - 20H = 0. Before winning the lottery, Y* = 0, so H = 12. After winning the $100 per day lottery, Y* = 100, so H = 7. Winning the lottery reduces this person's quantity of labor supplied by 5 hours when w = $10.
You might also like to view...
Other things remaining the same, if the expected future exchange rate rises, the demand curve for U.S. dollars shifts ________ and the supply curve of U.S. dollars shifts ________
A) rightward; rightward B) rightward; leftward C) leftward; rightward D) leftward; leftward
Potential problems with incentive based compensation are
a. not evaluating the relevant performance measures b. rewarding outcomes that are not include in the performance evaluation c. not funding rewards for meeting performance measures d. all of the above
Speculators serve no useful function in a market
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.6 below to answer the question that follows.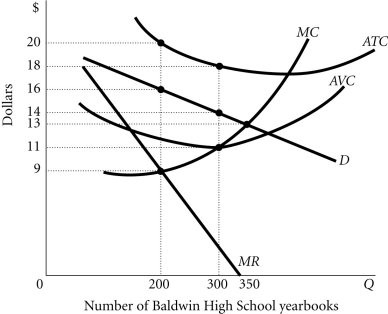 Figure 13.6 Refer to Figure 13.6. The profit-maximizing price for the Memory Company's high school yearbook is
Figure 13.6 Refer to Figure 13.6. The profit-maximizing price for the Memory Company's high school yearbook is
A. $0. B. $9. C. $16. D. $20.