Boyle’s law of gases helps explain the mechanics of breathing. What does Boyle’s law state?
a. For gases in a closed space, pressure and volume are positively correlated.
b. The volume occupied by an ideal gas is directly proportional to the number of molecules present.
c. For gases in a closed space, pressure and volume are inversely related.
d. The volume occupied by an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the number of molecules present.
c. For gases in a closed space, pressure and volume are inversely related.
You might also like to view...
In Figure 26.09 (above) the animals across are a lancelet, lamprey, salmon, lizard, and rabbit. If the salmon, lizard, and rabbit are an ingroup, which animals above would be an outgroup and which characteristics are necessary to be in the ingroup?
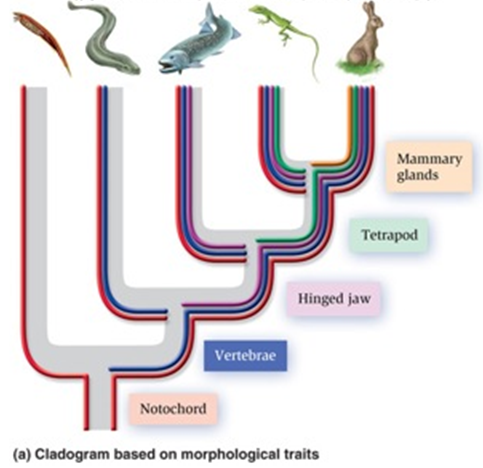
A. Lamprey and lancelet; notochord and vertebrae.
B. Lamprey only; vertebrae, hinged jaw, tetrapod, and mammary glands.
C. Lancelet and lamprey; hinged jaw, tetrapod, and mammary glands.
D. Lancelet, lamprey and salmon; hinged jaw, tetrapod, and mammary glands.
E. Lizard and rabbit; tetrapod and mammary glands.
Pseudonocardia is an organism that is hosted by
A. ants that cultivate fungal gardens. B. wood-eating insects. C. people with severe acne. D. marine invertebrates.
A cell containing two identical copies of a pair of homologous chromosomes undergoes meiosis, during which the non-sister chromatids in that pair crossover, exchanging a gene that controls the rate of cellular metabolism. After the resulting gametes combine with others to form a zygote, what will the effect of this crossover be?
a. The metabolism of the new organism will be increased. b. The organism will have inherited a defective copy of this gene. c. Exchanging identical genes will have no effect on metabolism. d. The metabolism of the new organism will be decreased.
The pericardium, or pericardial sac
A. is a double-layered, closed structure. B. anchors the heart in the mediastinum. C. has a tough fibrous connective tissue outer layer. D. has an inner layer of squamous epithelial cells. E. has all of these characteristics.