Between 1950 and 2004, standards of living in the OECD countries
A) did not change at all.
B) were converging.
C) all increased at the same rate.
D) decreased at the same rate.
E) decreased, but at different rates.
B
You might also like to view...
Over the past several decades, low-productivity and high-productivity workers in the US and other countries have tended to invest in their own human capital by completing more years of college than earlier generations
Which of the following reasons does NOT help to explain this trend? A) The cost of education for low-productivity workers has declined due to the emergence of online and other nontraditional programs. B) The earnings gap between workers with and without education has grown larger over time. C) The cost of education for high-productivity workers has increased over time. D) The benefit associated with increased education has increased over time.
cyclical unemployment is best defined as
a. deviation of unemployment from the natural rate b. unemployment dued to individuals searching for new jobs c. chronic unemployment dued to wages not balancing with goods and services d. unemployment associated with inefficiency in capital markets e. unemployment resulting from people who don't wish to work.
Which of the following would most likely discourage investment?
a) an increase in the selling price of a firm’s output b) a reduction in the selling price of corporate stock c) an increase in bond prices d) a reduction in the rate of inflation e) an increase in the optimal capital stock
Refer to the information provided in Figure 30.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.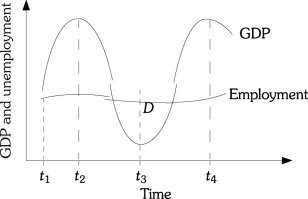 Figure 30.2Refer to Figure 30.2. Between times t3 and t4, labor is
Figure 30.2Refer to Figure 30.2. Between times t3 and t4, labor is
A. more productive because growth in employment exceeds growth in output. B. less productive because growth in employment is less than growth in output. C. more productive because growth in employment is less than growth in output. D. less productive because growth in employment exceeds growth in output.