Japan experienced periods of deflation — a declining price level — during the 1990s. During a deflationary period, which would be higher: nominal GDP or real GDP? Why? Assume that the base year of choice is prior to the deflationary period
What will be an ideal response?
Real GDP would be higher, as long as the base year was before the period of deflation. Nominal GDP would be measured using the lower prices that resulted from the deflation. Real GDP would use the higher prices before the deflation, assuming the base year was before the deflation.
You might also like to view...
Inflation can be started by
A) a decrease in aggregate supply or a decrease in aggregate demand. B) a decrease in aggregate supply or an increase in aggregate demand. C) an increase in aggregate supply or an increase in aggregate demand. D) an increase in aggregate supply or a decrease in aggregate demand. E) an increase in aggregate demand or an increase in potential GDP.
Tele-Com, Inc, the nation's largest cable TV company, tested the effect of a price reduction for the Disney Channel. It lowered prices from $10.75 to $7.95 and found that the number of customers more than doubled. This means the
a. demand curve for the Disney Channel shifted to the right. b. supply curve of the Disney Channel shifted to the left. c. demand for the Disney Channel is elastic in this price range. d. demand for the Disney Channel is inelastic in this price range.
The usual results of an adverse supply shock are
a. a rise in prices and a fall in output. b. a fall in prices and a rise in output. c. increased growth and lower inflation. d. higher net exports.
Figure 4-22
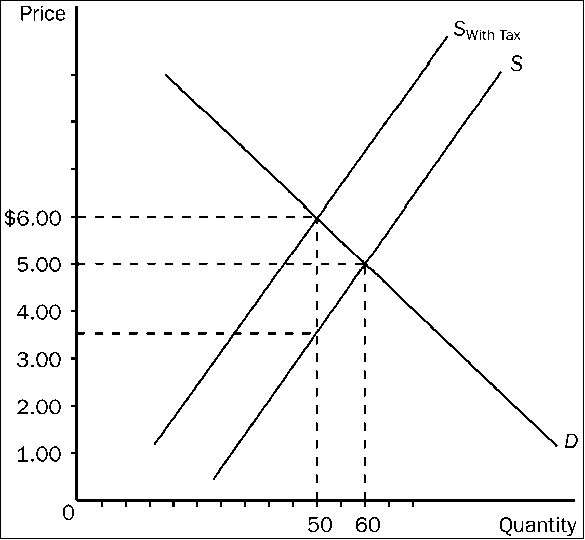
Refer to . The price paid by buyers after the tax is imposed is
a.
$1.00.
b.
$3.50.
c.
$5.00.
d.
$6.00.