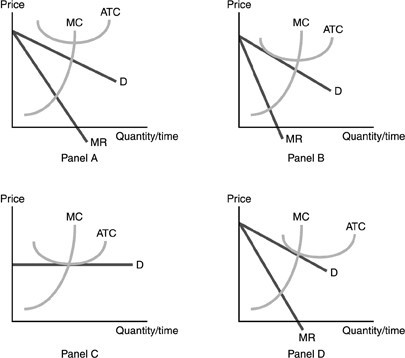
 Refer to the above figure. A long-run equilibrium in monopolistic competition is pictured by
Refer to the above figure. A long-run equilibrium in monopolistic competition is pictured by
A. Panel A.
B. Panel B.
C. Panel C.
D. Panel D.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Riskless transactions to take advantage of profit opportunities due to a price differential or a yield differential in excess of transaction costs are called
A) differential actions. B) cash transactions. C) arbitrage. D) forward transactions.
Suppose the economy's production function is Y = A(300N – N2). The marginal product of labor is MPN = A(300 - 2N). Suppose that A = 10. The supply of labor is NS = 0.05w + 0.005G
(a) If G is 26,000, what are the real wage, employment, and output? (b) If G rises to 26,400, what are the real wage, employment, and output? (c) If G falls to 25,600, what are the real wage, employment, and output? (d) In cases (b) and (c), what is the government purchases multiplier; that is, what is the change in output divided by the change in government purchases?
What is one way firms can enforce tie-in sales?
A) One of the goods has no close substitutes. B) contractual arrangements C) information asymmetry D) Any of the above.
The elasticity of supply coefficient for bicycles is estimated to be equal to 1.5 . It is expected, therefore, that a 4% increase in price would lead to:
a. a 4% decrease in the quantity of bicycles supplied. b. a 4% increase in the quantity of bicycles supplied. c. a 6% decrease in the quantity of bicycles supplied. d. a 6% increase in the quantity of bicycles supplied.