Exhibit 14-8 Aggregate demand and supply
?
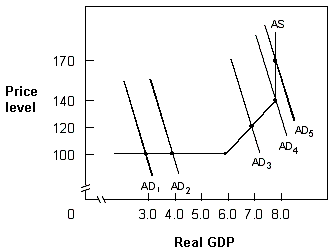
In Exhibit 14-8, when aggregate demand shifts from AD4 to AD5, the economy experiences:
A. cost-push inflation.
B. cost-pull inflation.
C. demand-push inflation.
D. demand-pull inflation.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The U.S. personal savings rate for the first quarter of 2012 dropped to its lowest level since the start of the recession. Americans stashed away 3.6 percent of personal income in the first quarter, down from 4
2 percent in the fourth quarter and a near-term peak of 6.2 percent in the second quarter of 2009. Which of the following could explain this drop in savings? A) a decrease in wealth from a fall in stock prices B) a rise in the real interest rate C) an increase in disposable income as the job market recovers D) a rise in consumer confidence that their incomes will be higher in the future
A secure strategy is a strategy that:
A. randomizes over two or more available actions in order to keep rivals from being able to predict a player's action. B. results in the highest payoff to a player regardless of the opponent's action. C. describes a set of circumstances in which no player can improve her payoff by unilaterally changing her own strategy, given the other players' strategies. D. guarantees the highest payoff given the worst possible scenario.
Which of the following would cause quantity demanded to change without changing the demand curve?
A. A change in the price of the good B. A change in the price of a substitute good C. A change in tastes and preferences D. A change in income
Which of the following best describes the cause-effect chain of an expansionary monetary policy?
A. A decrease in the money supply will lower the interest rate, increase investment spending, and increase aggregate demand and GDP. B. A decrease in the money supply will raise the interest rate, decrease investment spending, and decrease aggregate demand and GDP. C. An increase in the money supply will raise the interest rate, decrease investment spending, and decrease aggregate demand and GDP. D. An increase in the money supply will lower the interest rate, increase investment spending, and increase aggregate demand and GDP.