If you buy a gift without knowing what a person really wants or needs, you have demonstrated:
A. the incentive problem of gift-giving.
B. the necessity-identification problem of gift-giving.
C. the knowledge problem of gift-giving.
D. the negative trade problem of gift-giving.
Answer: C. the knowledge problem of gift-giving.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 4.2. The dominant strategy for Cameron is to
A) go to the movie theater. B) go to the bowling alley. C) go to either the movie theater or to the bowling alley. D) Cameron does not have a dominant strategy.
When the production possibilities frontier is bowed outwards, the opportunity cost of producing more of one good
A) increases in terms of the amount foregone of the other good. B) decreases in terms of the amount foregone of the other good. C) remains constant. D) cannot be determined.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the short run would be: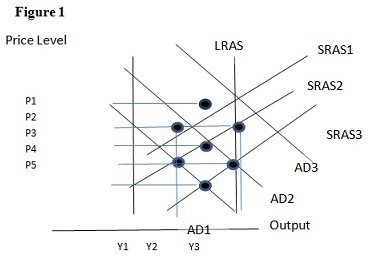
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y3. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y2.
Which of the following statements is accurate?
A. Fixed exchange rates greatly constrain a country's ability to pursue an independent monetary policy. B. Fiscal policy is highly effective with fixed exchange rates and unresponsive international capital flows. C. Contractionary monetary policy is effective under a fixed exchange-rate regime. D. Fiscal policy is not effective with fixed exchange rates in an environment of highly responsive international capital flows.