The charge cycle shown in Figure P2.10 is an example of a two-rate charge. The current is held constant at 70 mA for 1 h. Then it is switched to 60 mA for the next 1 h. Find:
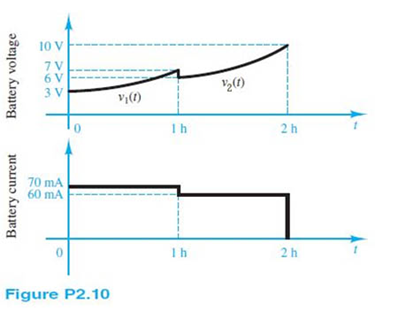
a. The total charge transferred to the battery.
b. The total energy transferred to the battery. Hint: Recall that energy w is the integral of power, or P = dw/dt.
Let

a) Current is equal to 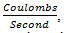
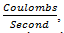 therefore given the current and a duration of that current, the transferred charge can be calculated by the following equation:
therefore given the current and a duration of that current, the transferred charge can be calculated by the following equation:
A?t=C
The two durations should be calculated independently and then added together.
0.070A?3600s=252C
0.060A?3600s=216C
252C+216C=468C
b) P=V•I, therefore, an equation for power can be found by multiplying the two graphs together.
First separate the voltage graph into two equations:

You might also like to view...
Define the equilibrium constant for pure water.
What will be an ideal response?
What are four important factors that should be considered when selecting a germination media?
What will be an ideal response?
The ____ is shorthand for the home directory, which typically has the same name as the user's account name.
A. backward slash (\) B. forward slash (/) C. dollar sign ($) D. tilde (~)
Gearbox ratio is the input speed divided by the output speed.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)