Refer to the diagram. Rational expectations theory says that a fully anticipated decrease in aggregate demand from AD 2 to AD 1 will:
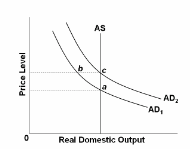
A. move the economy from a to b to c.
B. shift the AS curve to the left.
C. move the economy from c to a new equilibrium at b.
D. move the economy directly from c to a.
D. move the economy directly from c to a.
You might also like to view...
Aggregate expenditure is equal to
A) C - I - G - NX. B) Y + C + I + G + NX. C) C + I + G - NX. D) C + I + G. E) C + I + G + NX.
The "crowding-out effect" suggests that
A. tax increases are paid primarily out of saving and therefore are not an effective fiscal device. B. increases in government spending financed through borrowing will increase the interest rate and reduce private investment. C. it is very difficult to have excessive aggregate spending in our economy. D. consumer and investment spending always vary inversely.
Value added is the
A. Increase in market value of a product that takes place at each stage of the production process. B. Impact on third parties caused by market activities. C. Difference between nominal GDP and real GDP. D. Addition to GDP because nonmarket activities are captured.
Explain the difference between final and intermediate goods, and give an example of each
What will be an ideal response?