In the absence of externalities, the optimal distribution of resources occurs when production is at
a. P = MC
b. P = ATC
c. TR = TC
d. MC = MR
e. P = AFC
A
You might also like to view...
When the interest rate increases, the quantity demanded of money held to satisfy your
a. speculative motive rises b. precautionary motive rises c. transactions motive falls d. precautionary motive falls e. speculative motive falls
Economists refer to externalities as an example of market failure when:
a. markets do not consider social costs as part of overall costs. b. additional external costs are so high that the firm must shut down. c. private costs are the same as costs to society as a whole. d. citizens bring lawsuits to stop production that pollutes.
Which of the following is true when long-run equilibrium conditions are present in price-taker and competitive price-searcher markets?
a. MR = ATC in both price-taker and competitive price-searcher markets. b. P = ATC in price-taker markets; P = MC in competitive price-searcher markets. c. P = MC in both price-taker and competitive price-searcher markets. d. P = ATC in both price-taker and competitive price-searcher markets.
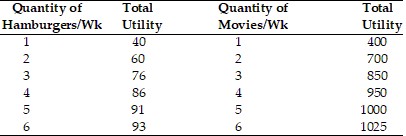 Refer to the above table. The price of a hamburger is $2, the price of a movie is $10, and the consumer has $44. What is the change in quantity demanded of hamburgers if the price of a hamburger decreases to $1?
Refer to the above table. The price of a hamburger is $2, the price of a movie is $10, and the consumer has $44. What is the change in quantity demanded of hamburgers if the price of a hamburger decreases to $1?
A. Quantity demanded increases by 2 hamburgers. B. Quantity demanded increases by 4 hamburgers. C. Quantity demanded increases by 1 hamburger. D. Quantity demanded increases by 3 hamburgers.