When effects are irreversible, it may be sensible to treat their possible causes even if they cannot be identified with certainty
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
T When effects are irreversible their consequences can be more severe, and this can justify more costly action such as treating possible causes.
You might also like to view...
Economic efficiency occurs when the firm produces a given output
A) by using the least amount of inputs. B) by using the maximum amount of inputs. C) at the least cost. D) at the greatest cost.
Which of the following never assumes, either implicitly or explicitly, independence between nominal and real variables?
A) the AS curve B) the Phillips curve C) Okun's law D) the classical dichotomy E) none of the above
Cindy discovers that when she goes to the beach, she does not have to bring her radio. She can put her blanket near someone who has a radio and listen all day (without having to carry her radio, get sand in her speakers, or buy new batteries). This is an example of:
a. private property abuse. b. external costs. c. a negative externality. d. a positive externality.
If the government set a price at $16, there would be price __________, that would cause a ___________ of ______ units.
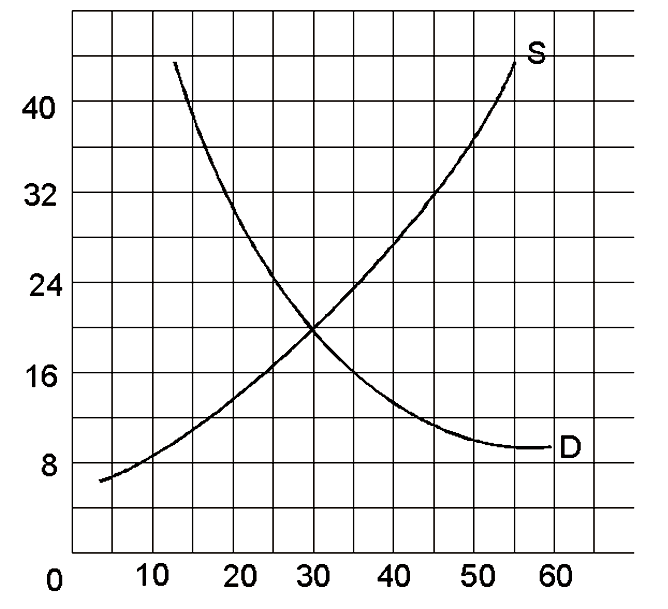
A. floor; shortage; 10
B. floor; surplus; 10
C. ceiling; shortage; 10
D. ceiling; surplus; 10