Ignoring income taxes and any minority interest effects, what is the amount of unrealized profit remaining from the intercompany sale of equipment at December 31, 2018?
King Corp. owns 80% of Kong Corp. and uses the cost method to account for its investment, which it acquired on January 1, 2018. The Financial Statements of King Corp. and Kong Corp. for the Year ended December 31, 2018 are shown below:
Income Statements

Retained Earnings Statements

Balance Sheets
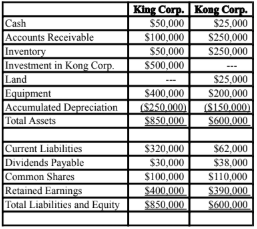
Other Information:
> King sold a tract of Land to Kong at a profit of $10,000 during 2018. This land is still the property of Kong Corp.
> On January 1, 2018, Kong sold equipment to King at a price that was $20,000 higher than its book value. The equipment had a remaining useful life of 4 years from that date.
> On January 1, 2018, King's inventories contained items purchased from Kong for $10,000. This entire inventory was sold to outsiders during the year. Also during 2018, King sold Inventory to Kong for $50,000. Half this inventory is still in Kong's warehouse at year end. All sales are priced at a 25% mark-up above cost, regardless of whether the sales are internal or external.
> Kong's Retained Earnings on the date of acquisition amounted to $350,000. There have been no changes to the company's common shares account.
> Kong's book values did not differ materially from its fair values on the date of acquisition with the following exceptions:
• Inventory had a fair value that was $20,000 higher than its book value. This inventory was sold to outsiders during 2018.
• A Patent (which had not previously been accounted for) was identified on the acquisition date with an estimated fair value of $15,000. The patent had an estimated useful life of 3 years.
• There was a goodwill impairment loss of $4,000 during 2018.
• Both companies are subject to an effective tax rate of 40%.
• Both companies use straight line amortization.
A) Nil. B) $15,000. C) $20,000. D) $10,000.
B) $15,000.
You might also like to view...
When thieves use your name and good credit rating to get cash or buy things, they are engaging in
A. Robin Hood theft. B. credit mishandling. C. credit exploitation. D. identity theft. E. misuse of standing.
Explain the Leontief Paradox.
What will be an ideal response?
Firms account for leases using either the operating lease method or the capital (finance) lease method. Which of the following is not true?
a. The capital, or finance, lease method treats leases equivalent to installment purchases or sales, where the lessee borrows funds from the lessor to purchase the asset and the lessor recognizes profit at the time of sale. b. The lessee records the leased asset and the lease liability on the balance sheet at the present value of the contractual cash flows at the time of signing the lease. c. The lessor amortizes the leased asset, similar to recognizing depreciation on buildings and equipment. d. The lessee recognizes interest expense on the lease liability, similar to recognizing interest expense on long-term notes or bonds. e. The lessor records the signing of a capital lease the same as if the lessor sold the leased asset for an installment note receivable.
Including a subject line in your e-mail message is optional because the message is usually short
Indicate whether the statement is true or false