If the outer air temperature in Problem 1.11 is –2°C, calculate the convection heat transfer coefficient between the outer surface of the window and the air assuming radiation is negligible.
GIVEN
• Window: 1 m by 3 m
• Thickness (L) = 7 mm = 0.007 m
• Surface temperatures
? Inner (Ti) = 20°C
? outer (To) = 17°C
• The rate of heat loss = 1040 W (from the solution to Problem 1.11)
• The outside air temperature = –2°C
FIND
• The convective heat transfer coefficient at the outer surface of the window ( h c)
ASSUMPTIONS
• The system is in steady state and radiative loss through the window is negligible
SKETCH
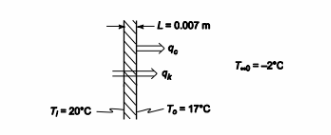
For steady state the rate of heat transfer by convection from the outer surface must
be the same as the rate of heat transfer by conduction through the glass
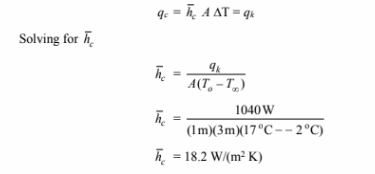
You might also like to view...
Match the words at the left to the correct blanks in the sentences at right. Use each choice only once.
A. A camera is an example of an instrument used for _________observations. B. _________ refers to telescopic observations in which we separate an object's light so we can measure its intensity at different wavelengths. C. If we want to confirm that a star's brightness alternately dims and brightens, we need __________ observations of the star. D. The familiar twinkling of the stars is caused by _____________, which also blurs telescopic images. E. Human civilization is responsible for what astronomers call ____________.
A large ice cube containing an iron railroad spike floats in a brim-full container of water. When the ice cube melts,
A) water spills over. B) no change in water level occurs. C) water level in the container drops.
Compare the prediction of the Bohr theory with the Schrödinger theory of the hydrogen atom concerning the angular momentum of the ground state (similarity or difference)
What will be an ideal response?
You are in a desert and you are thirsty. You come upon a deep well hole and you see water about 11 meters down. You take a long tube and you try to drink the water by sucking on the tube. Compared to drinking with a cup with a standard 20 cm straw, in this case, drinking would be
1.much easier. 2.about the same level of difficulty. 3.more difficult. 4.impossible.