A diatomic molecule has 2.6 × 10-5 eV of rotational energy in the L = 2 quantum state. What is the rotational energy in the L = 1 quantum state?
A)
3.4 × 10-6 eV
B)
4.1 × 10-6 eV
C)
5.3 × 10-6 eV
D)
7.8 × 10-6 eV
E)
8.7 × 10-6 eV
E
You might also like to view...
In an experiment involving the apparatus shown in figure Q4.1b, suppose that after shining light on the cathode long enough that the voltmeter settles down to a fixed value, we suddenly cut off the light. If the voltmeter is truly ideal, what happens to the value displayed? 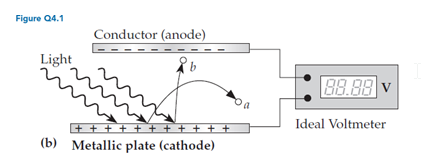
A. It immediately drops to zero. B. It slowly decays to zero. C. It remains fixed. D. It does something else. (Describe what.)
A uniformly charged rod (length = 2.0 m, charge per unit length = 3.0 nC/m) is bent to form a semicircle. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the center of the circle?
a. 64 N/C b. 133 N/C c. 48 N/C d. 85 N/C e. 34 N/C
What is cosmic background radiation evidence for?
a. Dark matter. b. Dark energy. c. The Big Bang theory. d. The theory of relativity. e. Neutrino oscillations.
When an ice skater twirling on the point of a skate draws her arms in she ends up whirling faster. This is because
A. linear momentum is conserved. B. angular momentum is conserved. C. rotational energy is conserved. D. a net external torque acts on the skater.