When an economy is not in equilibrium,
A) planned expenditures exceed production and income.
B) there is no savings nor investment.
C) government tax revenues equal planned government expenditures.
D) production and income equal planned expenditures.
A
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 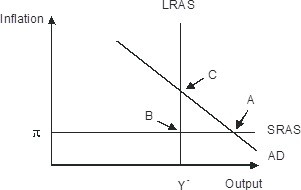
A. recessionary; A B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; B D. expansionary; A
The opportunity cost of holding excess reserves is equal to
A. the federal funds rate. B. the federal funds rate minus the discount rate. C. the discount rate. D. none of the above.
Microeconomics is defined as that part of economic analysis that
A) studies the behavior of the economy as a whole. B) includes the problems of inflation and unemployment. C) studies individual decision making by households and firms. D) concerns aggregate production and consumption.
One goal of rate-of-return regulation is the prevention of
A. free market entry. B. environmental degradation. C. positive economic profits. D. poor quality service.