Draw a profit/price trade-off curve that results from moving from a competitive to a monopoly industry organization. Show the equilibrium position for the regulator with a political support function (PS curve). What can we say about prices and profits of the regulated industry if it started as a monopoly?
What will be an ideal response?
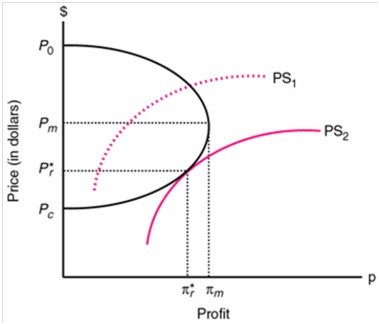
The above diagram shows the equilibrium position for the regulator with a political support function (PS curve). The dark curve shows the profit/price trade-off that a firm faces as it moves from a competitive industry to a monopoly. This political equilibrium results in a price greater than the price under a perfectly competitive market structure, but lower than the price under a monopoly market structure. If this industry was originally an unregulated monopoly, then prices and industry profits will be lower under regulation.
You might also like to view...
Discretionary fiscal policy is defined as fiscal policy
A) left to the discretion of military authorities. B) initiated by an act of Congress. C) initiated by a Presidential proclamation. D) triggered by the state of the economy. E) with multiplier effects.
If the revenues from a Pigovian tax are not directed to those who are affected by the externality, the outcome:
A. is efficient and maximizes surplus. B. is not efficient and does not maximize surplus. C. is not efficient and maximizes surplus. D. is efficient, but does not maximize surplus.
A rightward shift of the investment demand curve might be caused by:
A. an increase in the price level. B. a decline in the real interest rate. C. businesses planning to increase their stock of inventories. D. an increase in business taxes.
Which type of cost does not depend on a firm's output?
A. fixed cost B. total cost C. variable cost D. marginal cost