An object 15 cm high is placed 15 cm in front of a convex mirror with a focal length of ?10 cm. What is the image height (in cm)?
a. 2
b. 4
c. 6
d. 8
e. 30
c
You might also like to view...
Torque: A flat rectangular loop of wire is placed between the poles of a magnet, as shown in the figure. It has dimensions w = 0.60 m and L = 1.0 m, and carries a current I = 2.0 A in the direction shown. The magnetic field due to the magnet is uniform and of magnitude 0.80 T. The loop rotates in the magnetic field and at one point the plane of the loop is parallel to the field. At that instant, what is the magnitude of the torque acting on the wire due to the magnetic field?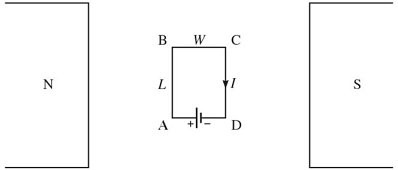
A. 0.00 N ? m B. 0.40 N ? m C. 0.48 N ? m D. 0.83 N ? m E. 0.96 N ? m
The force exerted on an electron moving in a magnetic field is maximum when the electron moves
A) parallel to the magnetic field. B) perpendicular to the magnetic field. C) either of these D) neither of these
A certain spherical asteroid has a mass of 3.5 × 1016 kg and a radius of 8.8 km. What is the minimum speed needed to escape from the surface of this asteroid? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ? m2/kg2)
A) 23 m/s B) 16 m/s C) 520 m/s D) 730 m/s
What does the equivalence principle say?
A) Gravity is the same thing as curvature of spacetime. B) The effects of gravity are exactly equivalent to the effects of acceleration. C) You cannot distinguish between motion at constant velocity and weight in a gravitational field. D) The effects of relativity are exactly equivalent to those predicted by Newton's laws of motion. E) All observers must always measure the same (equivalent) weights for moving objects.