Alan is sitting in a bar drinking beers that cost $4 each. According to the economic decision rule, Alan will stop drinking when the marginal:
A. cost remains at $4.
B. benefit to him of an additional beer is less than $4.
C. cost to him of an additional beer is less than the marginal benefit.
D. benefit to him of an additional beer is greater than $4.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose the government levies a per-unit tax on TVs, and this tax increases the price of TVs by $10. a. On a graph with TVs on the horizontal axis and "$'s of other consumption" on the vertical, illustrate how the budget constraint for a consumer with exogenous income changes as a result of the tax. b. Suppose you know the bundle on the after-tax budget that is chosen by the consumer. Illustrate on your graph how much in tax revenue the government is raising from this consumer. c. If the government replaced the tax on TVs with a lump sum tax that does not alter any prices but raises the same amount of revenue from the consumer, how would this consumer's budget constraint change?
What will be an ideal response?
Downsizing is the practice of laying off workers in an attempt to decrease average total cost. Can laying off workers decrease average total cost? Is it possible for the firm to downsize and have its average total cost increase? Explain your answer
What will be an ideal response?
The quantity theory of money is the idea that in the long run
A) the quantity of money is determined by banks. B) the quantity of money serves as a good indicator of how well money functions as a store of value. C) the quantity of money determines real GDP. D) an increase in the growth rate of the quantity of money leads to an equal increase in the inflation rate.
Refer to the accompanying figure. An increase in supply is represented by a shift from: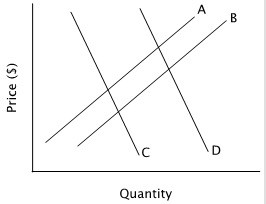
A. curve B to curve A. B. curve C to curve D. C. curve C to curve B. D. curve A to curve B.