What are institutions? What is the institutions hypothesis of economic growth?
What will be an ideal response?
Institutions are the formal and informal rules governing the organization of society, including its laws and regulations. The institutions hypothesis claims that differences in institutions, that is, the way in which societies have organized themselves and shaped the incentives of individuals and businesses, are at the root of the differences in prosperity across the world.
You might also like to view...
The major difficulty with using a tax on pollution instead of a fixed percentage reduction regulation is:
A. that it only works in theory. B. that firms would not pay the tax. C. establishing the optimal size of the tax. D. that it would cause prices to rise.
If a firm decreases its capital stock, real wages will likely ________ and the equilibrium quantity of labor will likely ________
A) decrease; increase B) increase; increase C) decrease; decrease D) increase; decrease
If the selling price of a firm's product is $500 and the estimated average cost of producing this product is $400, what is the firm's markup?
A) 15 percent B) 20 percent C) 25 percent D) 40 percent
A price ceiling of $8 placed on the market in the graph shown:
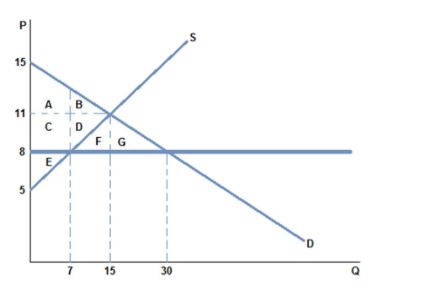
A. is non-binding, and does not affect the market.
B. is binding, and causes a shortage.
C. is binding, and causes a surplus.
D. is non-binding, and does not prevent the market from reaching equilibrium.