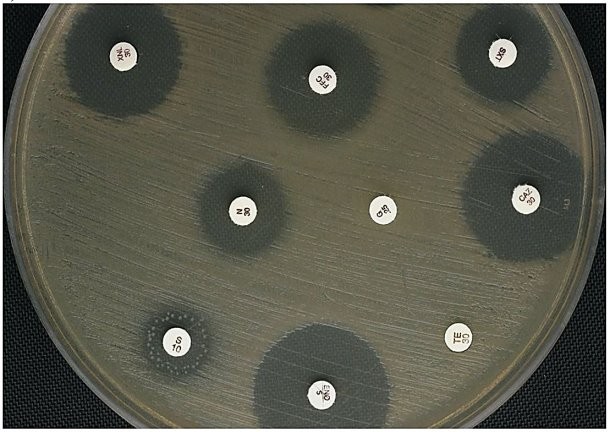
 Examine the diffusion susceptibility plate results shown in Figure 10.2. Propose an explanation for the appearance of the zone around the S/10 disk, and discuss the implications for therapeutic use of this antibiotic for the pathogen tested.
Examine the diffusion susceptibility plate results shown in Figure 10.2. Propose an explanation for the appearance of the zone around the S/10 disk, and discuss the implications for therapeutic use of this antibiotic for the pathogen tested.
What will be an ideal response?
The ring of colonies within the outermost limit of the zone of inhibition indicates that there are some cells in the population that are less susceptible to the antibiotic than the rest. If this antibiotic were used to treat an infection with this population, the growth of bacteria with some resistance would be promoted at the expense of the more susceptible cells, potentially giving rise to a new variant that is fully resistant. If this were to occur in a patient being treated, the antibiotic therapy would fail, putting the patient's health at risk. Therefore, drug AM would be a poor choice, perhaps the poorest choice, for chemotherapy against this bacterial species.
You might also like to view...
Are any of the offspring or parents affected?
a. Yes b. No
In contrast to predation, a parasite usually ____
a. does not kill its host b. always kills its host c. is a short-term visitor d. is larger than its host e. does not harm its host
During a study session about evolution, one of your fellow students remarks, "The giraffe stretched its neck while reaching for higher leaves; its offspring inherited longer necks as a result." Which statement is most likely to be helpful in correcting this student's misconception?
A. Disuse of an organ may lead to its eventual disappearance. B. Only favorable adaptations have survival value. C. If the giraffes did not have to compete with each other, longer necks would not have been passed on to the next generation. D. Characteristics acquired during an organism's life are generally not passed on through genes. E. Spontaneous mutations can result in the appearance of new traits.
A group of ten tomato plants are germinated and maintained in a large tray with no drainage. After several weeks they all begin to wilt and die despite repeated watering and fertilization. The most likely cause of this die-off is _____
A) competition for resources B) a lack of oxygen for the roots C) organic nutrient depletion D) no room left for root growth