Elastic Collisions: In the figure, determine the character of the collision. The masses of the blocks, and the velocities before and after, are shown. The collision is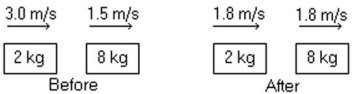
A. perfectly elastic.
B. partially inelastic.
C. completely inelastic.
D. characterized by an increase in kinetic energy.
E. not possible because momentum is not conserved.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The drawing below shows a sequence of Stern–Gerlach devices. By analogy to the cases discussed in the chapter, what do you think are the probabilities that an electron entering the last device will come out of that device’s plus and minus channels, respectively? 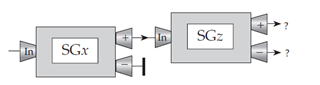
A. 1 and 0, respectively (AA if reversed, i.e., 0 and 1)
B. 0.933 and 0.067, respectively (BB if reversed)
C.  , respectively (CC if reversed)
, respectively (CC if reversed)
D.  for both channels
for both channels
E. Some other probabilities (specify)
Regarding the relation between acceleration, force, and mass, an object's acceleration is
A) inversely proportional to the force on it and proportional to the object's mass. B) proportional to the inverse of the height of the Empire State Building. C) proportional to the force on it and inversely proportional to the object's mass. D) proportional to the force on it and proportional to the object's mass. E) inversely proportional to the force on it and inversely proportional to the object's mass.
An acoustical engineer designing a music hall is most concerned with
A) modulation. B) forced vibrations. C) resonance. D) beats. E) reverberations.
A product of incomplete combustion that is a major air pollutant is
a. H2O. b. O2. c. NOx. d. CO.