Liability management refers to:
A. a bank's handling of the assets in individual trust funds.
B. how a bank attracts deposits and what it pays for them.
C. how a bank manages its accounts receivable.
D. a bank's handling of loans and other assets.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A decrease in households' disposable income ________ saving supply, and the supply of loanable funds curve ________
A) increases; shifts rightward B) decreases; shifts leftward C) increases; shifts leftward D) does not change; does not shift E) decreases; shifts rightward
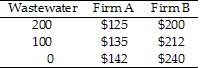
 Consider the data in Table 9.6. Both firms can benefit if Firm A sells its pollution permit allowing it to generate 100 gallons of wastewater to Firm B for:
Consider the data in Table 9.6. Both firms can benefit if Firm A sells its pollution permit allowing it to generate 100 gallons of wastewater to Firm B for:
A. a price between $7 and $12. B. a price between $0 and $7. C. a price between $12 and $18. D. Both firms cannot benefit if A sells permits to B.
Suppose your bank pays you 5 percent interest per year on your savings account. If prices increase by 5 percent per year over that time, approximately how much real value do you gain by keeping $100 in the bank for a year?
A. $0 B. $1 C. $3 D. $6
For most commonly used social welfare functions, an efficient allocation is
A) always preferred over any inefficient allocation. B) not possible. C) usually preferred. D) never preferred.