Explain the relationship between coupon rate (or coupon yield) and current yield.
What will be an ideal response?
The coupon rate is simply the annual coupon divided by the face value. The current yield is the annual coupon divided by the price of the bond. The only time these should equal each other is when the price of the bond equals the face value. If the price is greater than the face value the current yield should be less than the coupon rate. If the price of the bond is less than the face value, the current yield should be greater than the coupon rate.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Horizontal Merger. If area F + G is larger than area E, we can conclude that the horizontal merger
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the effects of a horizontal merger. Before the merger, the firm behaves competitively producing Q0 and charging P0. The merger lowers the firm's marginal cost and gives the firm enough market power to switch to the monopoly equilibrium.
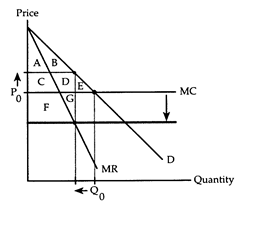
a. will reduce economic efficiency.
b. causes both consumers' and producer's surplus to rise.
c. will not increase the firm's profit and thus will not be undertaken.
d. creates an increase in social gain.
Suppose the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium and aggregate demand rises. In the long run prices
a. and output are higher than in the original long-run equilibrium. b. and output are lower than in the original long-run equilibrium. c. are higher and output is the same as the original long-run equilibrium. d. are the same and output is lower than in the original long-run equilibrium.
The theoretical proposition that government deficits do not affect the level of output because individuals realize that they have to pay the deficits in the future, and therefore increase their savings now, is called:
A. purchasing power parity. B. functional finance. C. sound finance. D. the Ricardian equivalence theorem.
The long-run supply curve in a constant-cost industry would be:
A. downsloping. B. upsloping. C. horizontal. D. vertical.