If the producer is at combination B as shown in Table 3-2, the opportunity cost of increasing corn production by 1 unit is
A. 29 units of cotton.
B. 5 units of cotton.
C. 12 units of cotton.
D. 4 units of cotton.
E. 1 unit of cotton.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Mexico and the members of OPEC produce crude oil. Realizing that it would be in their best interests to form an agreement on production goals, a meeting is arranged and an informal, verbal agreement is reached. If both Mexico and OPEC abide by the agreement, then OPEC's profit will be $200 million and Mexico's profit will be $100 million. If both Mexico and OPEC cheat on the agreement, then OPEC's profit will be $175 million and Mexico's profit will be $80 million. If only OPEC cheats, then OPEC's profit will be $185 million, and Mexico's profit will be $60 million. If only Mexico cheats, then Mexico's profit will be $110 million, and OPEC's profit will be $150 million. You may find it helpful to fill in the payoff matrix below. src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/ppg__rrr0818190951__f1q385g1.jpg" alt="" style="vertical-align: 0.0px;" height="203" width="377" />This game is ________ because ________.
A. not a prisoner's dilemma; cheating is better for both
B. a prisoner's dilemma; not cheating is better for both
C. not a prisoner's dilemma; OPEC does not have a dominant strategy
D. a prisoner's dilemma; cheating is better for both
Suppose Bank A holds $200 of reserves, has deposits of $1000, and the desired reserve ratio is 20 percent. How many deposits can Bank A create?
A) zero, because Bank A has no excess reserves B) $200 C) $800 D) $400
The idea that MPCs are different in different stages of a person's life is called
a. Keynes's absolute income hypothesis b. Duesenberry's relative income hypothesis c. Friedman's permanent income hypothesis d. the life-cycle hypothesis of consumption e. the consumption function
What would the situation be at $1.25 = 1 euro?
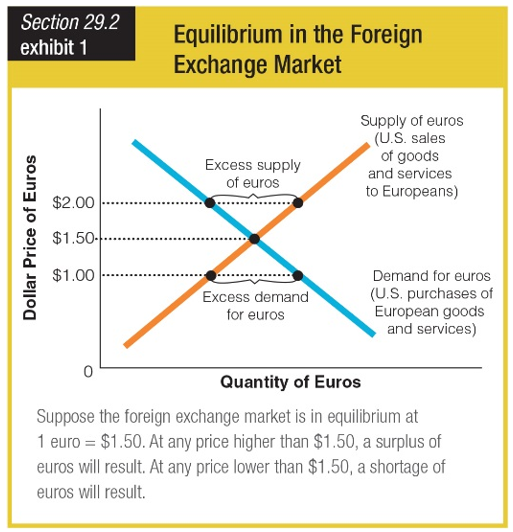
a. The value of $1 would be 1.25 euros.
b. The quantity of euros demanded would be greater than the quantity supplied.
c. The foreign exchange market would be in equilibrium.
d. The quantity of euros supplied would be greater than the quantity demanded.