Gains from the Single European Act were expected to be from
A) reduction of transactions costs from having a single currency.
B) reduced trade barriers and customs problems.
C) increased competition and economies of scale.
D) harmonization of environmental and labor standards.
C
You might also like to view...
If the cost of acquiring more information outweighs the benefit of having more information about a good, then we can predict:
A. the exchange will definitely not take place. B. the exchange may take place anyway. C. the exchange will not benefit anyone. D. the exchange will take place, but will be regretted in the future.
The opportunity cost of a movement from point N to J would
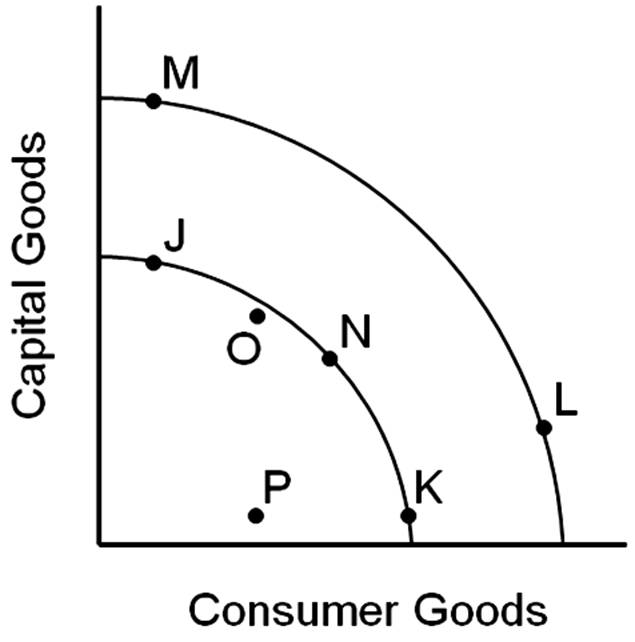
A. be the lost production of some capital goods.
B. be the lost production of some consumer goods.
C. be slower economic growth in the future.
D. not involve any sacrifice of either capital or consumer goods.
Some studies find that trade in the Eurozone has risen substantially, but compared with the control group of nations that stayed out, Baldwin finds the effect is:
A) larger (25%) because prices have fallen and trade has increased by much more than the control group. B) just about the same because the control group is very similar to nations in the Eurozone. C) somewhat larger (9%) because there has been no measurable price decline within the union or evidence of trade diversion. D) much smaller (-2%) because trade within the union has been lackluster, whereas trade with the control group has increased dramatically.
If products A and B are complements and the price of B decreases, the:
A. demand for A will decline and the demand for B will increase. B. demand for A will increase and the amount of B demanded will increase. C. demand curves for both A and B will shift to the left. D. amount of B purchased will increase, but the demand curve for A will not shift.