The graphs below show the frequency of the b+ allele over twenty generations in two populations of heterozygous
flour beetles (data for a population of ten individuals is shown in graph A; data for a population of one hundred
individuals is shown in graph B). Why does the frequency of the b+ allele increase in both populations?
a. b+ is a lethal allele
b. b+ is a balanced polymorphism
c. b+ is a fixed allele
d. the b+ allele is adaptive
e. b+ is a neutral mutation
ANSWER: d
You might also like to view...
The multiple sites of DNA replication along eukaryotic chromosomes are known as
A) replicons. B) multireplication forks. C) helicase loaders. D) ARS elements. E) none of the above
When performing quality control on motility media, which of the following organisms should be used?
a. Acidovorax facilis and Sphingomonas spp. b. Centers for Disease Control and Preven-tion (CDC) group IIc and CDC group IIe c. CDC group Iii and Sphingobacterium mi-zutaii d. CDC group IIh and A. facilis
Which of the following is an example of a noncommunicable infectious disease?
A. Influenza B. Urinary bladder infection C. Diabetes mellitus D. Strep throat
In Figure 17-1, the purpose of growing the donor cells in nutrient-limited media is:
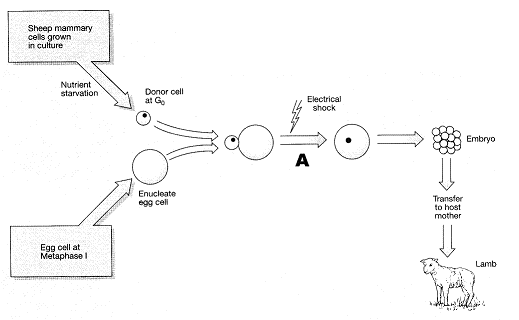
a. to have small cells that would be easier to manipulate.
b. to replicate a normal environment.
c. to force the donor cell nucleus into the G0 cell stage.
d. to induce favorable mutations.
e. to initiate apoptosis.