"In the long run, there are no fixed costs.". Explain the statement
There are no fixed costs in the long run. Given time, the processes used to provide goods and services to customers can change. For example, a firm can build new factories and purchase new machinery or it can close existing facilities. In planning for the long run, the firm will compare alternative production combinations and change its production process to the combination that produces the desired output at the lowest possible cost. A failure to make these adjustments over time can result in a loss of customers and sales to competing firms that have adopted the most cost-effective production methods and produce newer and better products.
You might also like to view...
Normative economics is
A) analysis involving value judgments about economic policies; or a statement of "what ought to be." B) analysis that is strictly limited to making either purely descriptive statements or scientific predictions. C) analysis of the behavior of the economy as a whole. D) decision making undertaken by households and business firms.
Bank regulators impose capital requirements in order to
a. increase the amount of leverage in the economy. b. provide an incentive for banks to hold risky assets. c. ensure banks can pay off depositors. d. increase the probability of a credit crunch.
If GDP is $36,000 and velocity is 3, the money supply is
A. $27,000. B. $12,000. C. $4,000. D. $3,000.
Which of the following statements describes the situation for the United Kingdom at a real interest rate of 4 percent?
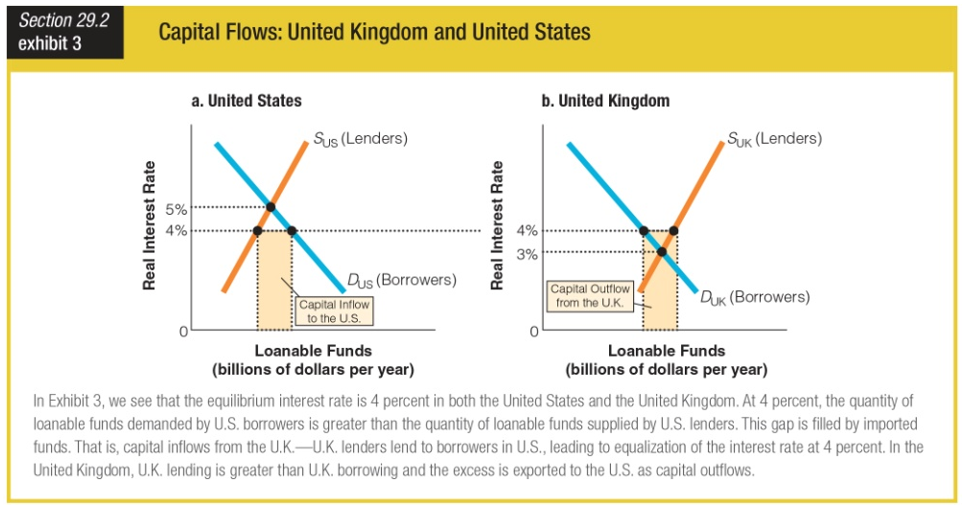
a. There is a capital inflow from the United States to the United Kingdom.
b. The quantity of loanable funds supplied by United Kingdom lenders is greater than the quantity demanded by United Kingdom borrowers.
c. The interest rate is at the equilibrium level for the United Kingdom.
d. U.K. borrowing is greater than U.K. lending, and the excess is exported to the United States as a capital outflow.