Marginal cost is defined as:
A. total variable cost resulting from a one-unit increase in quantity.
B. quantity resulting from a one-unit increase in total variable cost.
C. the change in total cost resulting from a one-unit increase in the change in quantity.
D. the change in quantity resulting from a one-unit increase in the change in total variable cost.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Suppose one county in Missouri decides it wants to reduce alcohol consumption, so the county passes a law that raises the price of a bottle of beer by $1 . As a result, people drive to other counties to drink alcohol, which results in an increase in drunk driving. This illustrates the principle that people respond to incentives
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Depending on the size of the multiplier and crowding-out effects, the rightward shift in aggregate demand from a tax cut could be larger or smaller than the tax cut
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
In the equation for the production function Y/L represents
a. productivity. b. output. c. the availability of natural resources. d. the amount of human capital.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.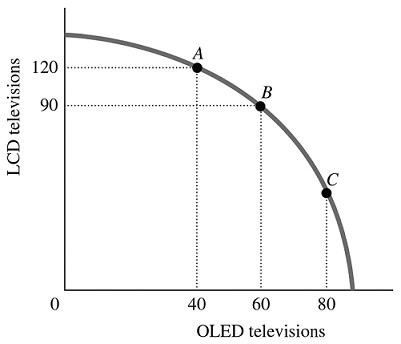 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
A. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 60 additional OLED televisions. B. 90 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions. C. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions. D. 120 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 40 additional OLED televisions.