A firm that has economies of scale:
a. at low output and but diseconomies of scale at high output is a natural monopoly.
b. at any particular level of output is a natural monopoly.
c. over the entire range of output demanded is a natural monopoly.
d. has a continually rising long-run average cost curve.
c. over the entire range of output demanded is a natural monopoly.
You might also like to view...
A decrease in a country's capital stock occurs when ________.
A. businesses sell machinery and equipment to one another B. the consumption of fixed capital exceeds gross domestic investment C. the prices of investment goods rise faster than the prices of consumer goods D. businesses have larger inventories at the end of the year than they had at the start
In 2006, before the start of the recession, the employment—population ratio was 63.4 percent. In August 2015, more than six years after the end of the recession, the ratio
A) was still only 59.4 percent. B) was back to its 2006 level. C) had increased to 72.3 percent. D) was still 50 percent lower than the ratio in 2006.
Parity pricing refers to
a. a price floor that creates a desired relationship between the prices farmers have to pay for goods they buy and the prices they get for goods they sell b. a price ceiling that creates a desired relationship between the prices farmers have to pay for goods they buy and the prices they get for goods they sell c. the subsidization of farm prices in markets where new technology is adapted d. the government's price intervention to create parity among various farm product prices, such as the price per bushel of corn, wheat, or soybeans e. the government's price intervention to create income equality (or parity) among farms producing identical goods, such as corn or cotton, according to farm size
Refer to the information provided in Figure 24.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow.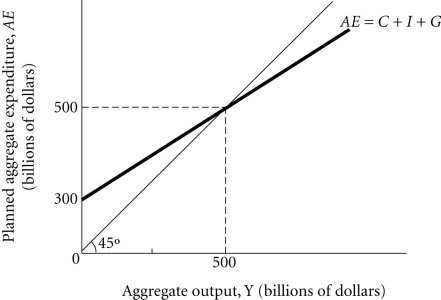 Figure 24.3Refer to Figure 24.3. If autonomous planned expenditure increases by $20 billion, equilibrium aggregate output ________ to $________ billion.
Figure 24.3Refer to Figure 24.3. If autonomous planned expenditure increases by $20 billion, equilibrium aggregate output ________ to $________ billion.
A. increases; 640 B. increases; 550 C. decreases; 360 D. increases; 600