Briefly discuss the following network topologies: daisy chain, star, bus, and ring.
What will be an ideal response?
A daisy chain topology, also called series or linear, is one of the earliest wiring methods. It is wired in series like Christmas tree lights.
Star, or common splice, is the most popular topology for home LANs. All modules on the network are connected to a single point with a separate wire from each module. Modules communicate with one another through a hub, router, or switch. The star configuration allows for easy addition of modules to the network by plugging a device into the central processor. A fault in a star system will result in failure of only the affected component.
Bus topology uses less cabling than star topology. A single main run bus cable is connected to all of the modules. Terminators provide resistance that absorbs frames once they have been transmitted so they are not received again. The terminators can be at each end of the bus or can be inside two of the nodes.
Ring, or loop, topologies are wired in series, but messages can travel either way in the network so a single break will not open the circuit.
You might also like to view...
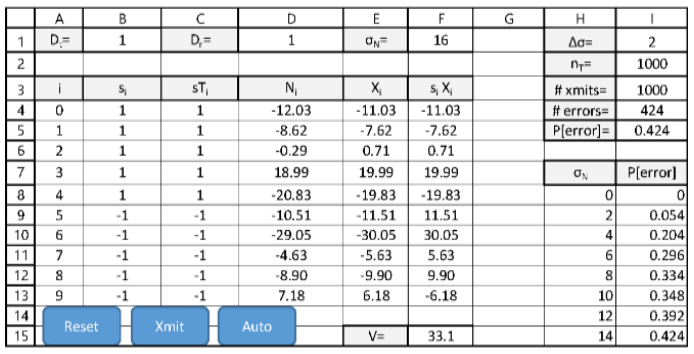
Probability of Error for complementary signals as function of ?N. The following worksheet specifies a 10-sample binary data signal s1 in B4:B13. A random transmitted bit Dt is computed in B1. The transmitted signal sTi (in C4:C13) = si if Dt=1 and =-si if Dt=0. The Gaussian noise sequence Ni SD ?N is specified in F1. The detected signal Xi is computed in E4:E13. The matched processor component siXi is computed in F4:F13, and the matched processor output V is computed in F15. The detected bit Dr is computed in D1.
The probability of error is estimated by computing the ratio of errors to transmitted data in I5 as
the noise ?N varies from 0 to 14?? in steps of ?? specified in I1. The total number of data bits to
be transmitted nT is specified in I2. The number of transmissions accomplished in shown in I3
and the number of errors in I4. Three VBA Macros are present:
? ResetCS resets the counts in I3 and I4.
? XmitCS increments the number of transmissions and, if an error occurs, increments the
error count.
? AutoCS computes the P[error] for nT transmissions as ?N varies and displays the results in
H8:I15.
a. What is the formula that computes Dt
in B1?
b. What is the formula that computes the transmitted signal sT2 in C6?
c. What is the formula that computes the noise component N2 in D6?
d. What is the formula that computes the detected signal X2 in E6?
e. What is the formula that computes the processor component s2X2 in F6?
f. What is the formula that computes the processor output V in F15?
g. What is the formula that computes Dr
in D1?
h. What is the formula that computes P[error] in I6 that produces 0 for #mits = 0?
i. Compose ResetCS.
j. Compose XmitCS.
k. Compose AutoCS.
Insulation lagging work would likely be found at a _____.
a. school b. petrochemical plant c. hospital d. big-box store
A(n)____ nut allows a cotter pin to be used.
A. castle-headed B. well C. acorn D. stake
Technician A says double-wall steel brake tubing is the only type of tubing approved for brake lines. Technician B says to use 100 percent copper tubing as a replacement. Who is correct?
A. A only B. B only C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor B