When you hire a company to paint your house, you cannot be sure of the quality of paint that was used. This situation is an example of
a. moral hazard.
b. the adverse selection problem.
c. the market for lemons.
d. the principal-agent problem.
d. the principal-agent problem.
You might also like to view...
Accelerator theory refers to the theory of
A) consumption that emphasizes that current consumer spending depends positively on the expected future growth of GDP. B) investment that emphasizes that current investment spending depends positively on the expected future growth of government spending. C) consumption that emphasizes that increases in consumption spending will result, through the multiplier effect, in greater increases in GDP. D) investment that emphasizes that current investment spending depends positively on the expected future growth of GDP.
Suppose the only characteristic of beer that a consumer cares about is alcohol content. Currently, Bud Light and Miller Lite have the same alcohol content.
a. Using 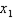
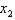
lowers its alcohol content by 50%. How would you change the utility function to account for this? c. Derive the MRS for the functions in (a) and (b) --- and interpret your answer. What will be an ideal response?
When a firm exits a monopolistically competitive market, the individual demand curves faced by all remaining firms in that market will
a. shift in a direction that is unpredictable without further information. b. shift to the right. c. shift to the left. d. remain unchanged. It is the supply curve that will shift.
A perfectly competitive firm breaks even at the level of output where
A. P = ATC. B. P = MC. C. P > ATC. D. P < ATC.