At its current level of production a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market receives $12.50 for each unit it produces and faces an average total cost of $10 . At the market price of $12.50 per unit, the firm's marginal cost curve crosses the marginal revenue curve at an output level of 1,000 units. What is the firm's current profit? What is likely to occur in this market and why?
Profit can be calculated as (P-ATC)xQ. ($12.50-10)x1,000 = $2,500 . Firms are likely to enter this market because existing firms are earning economic profits.
You might also like to view...
From the data given in Table 3-2, the opportunity cost of increased cotton in moving from A to B is
A. 16 units of corn. B. 31 units of corn. C. 15 units of corn. D. 4 units of corn. E. 1 unit of corn.
In the presence of positive externalities, the market will choose a price that is __________ and produce a quantity that is __________ than the socially optimal price and quantity
a. higher; lower b. lower; lower c. higher; higher d. lower; higher e. impossible to know without more information about market demand and supply
Lorna's Lumberyard is a monopsony. Lorna estimates that at a wage of $10 per hour, 100 workers would be willing to work for her. Similarly, at a wage of $12 per hour, 200 workers would be willing to work. Her marginal labor cost is
a. $10 b. $14 c. $120 d. $140 e. $240
When the overall price level decreases, what is the effect on the economy?
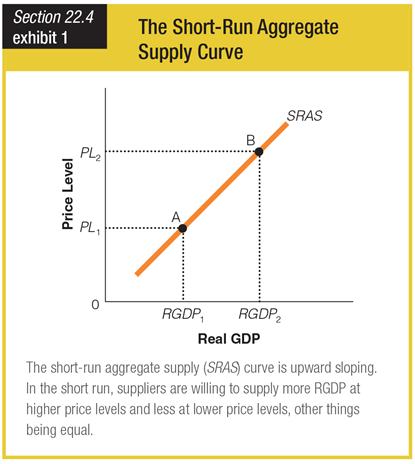
a. There is an increase in the quantity of real GDP that producers are willing and able to supply.
b. Producers are willing and able to supply less real output.
c. Movement occurs along the short-run aggregate supply curve from point A to point B.
d. The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.