A standard 4 10 cm steel pipe (ID = 10.066 cm., OD = 11.25 cm) carries superheated steam at 650°C in an enclosed space where a fire hazard exists, limiting the outer surface temperature to 38°C. To minimize the insulation cost, two materials are to be used; first a high temperature (relatively expensive) insulation is to be applied to the pipe and then magnesia (a less expensive material) on the outside. The maximum temperature of the magnesia is to be 315°C. The following constants are known.

(a) Specify the thickness for each insulating material.
(b) Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient based on the pipe OD.
(c) What fraction of the total resistance is due to (1) steam-side resistance, (2) steel pipe
resistance, (3) insulation (combination of the two), and (4) outside resistance?
(d) How much heat is transferred per hour, per foot length of pipe?
GIVEN
• Steam filled steel pipe with two layers of insulation
• Pipe inside diameter (Di) = 10.066 cm=0.10066 m
• Pipe outside diameter (Do) = 11.25 cm=0.1125 m
• Superheated steam temperature (Ts) = 650°C
• Maximum outer surface temperature (Tso) = 38°C
• Maximum temperature of the Magnesia (Tm) = 315°C
• Thermal conductivities
? High-temperature insulation (kh) = 0.1 W/(m K)
? Magnesia (km) = 0.076 W/(m K)
? Steel (ks) = 43 W/(m K)
• Heat transfer coefficients
? Steam side ( ci h ) = 500 W/(m2 K)
? Outside ( co h ) = 11 W/(m2 K)
• Ambient temperature (Ta) = 21°C FIND
(a) Thickness for each insulation material
(b) Overall heat transfer coefficient based on the pipe OD (c) Fraction of the total resistance due to
? Steam-side resistance
? Steel pipe resistance
? Insulation
? Outside resistance (d) The rate of heat transfer per unit length of pipe (q/L) ASSUMPTIONS
• The system is in steady state
• Constant thermal conductivities
• Contact resistance is negligible
SKETCH
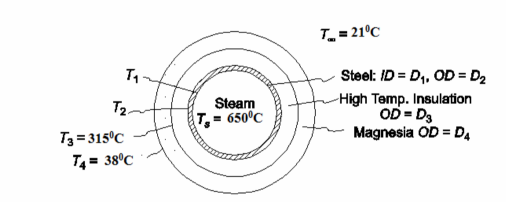
The thermal circuit for the insulated pipe is shown below
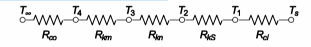
The values of the individual resistances can be evaluated
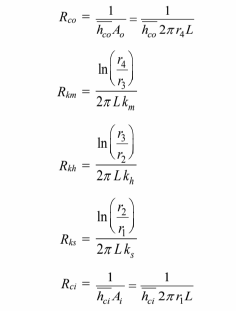
The variables in the above equations are
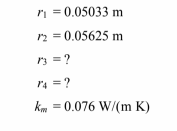
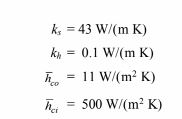
The temperatures for this problem are
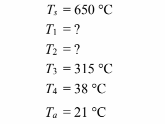
There are five unknowns in this problem: q/L, T1, T2, r3, and r4. These can be solved for by writing the
equation for the heat transfer through each of the five resistances and solving them simultaneously.
1. Steam side convective heat transfer
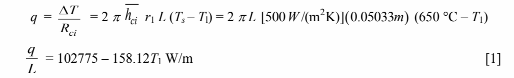
2. Conduction through the pipe wall
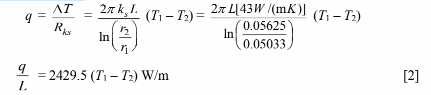
3. Conduction through the high temperature insulation
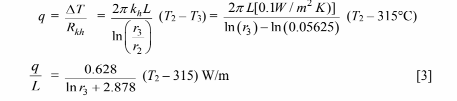
4. Conduction through the magnesia insulation
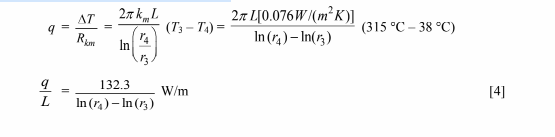
5. Air side convective heat transfer
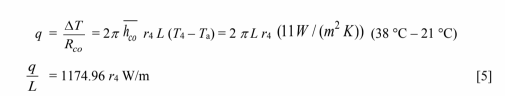
To maintain steady state, the heat transfer rate through each resistance must be equal. Equations [1] through [5]
are a set of five equations with five unknowns, they may be solved through numerical iterations using a simple program or may be combined algebraically as follows
Substituting Equation [1] into Equation [2] yields

Substituting this into Equation [3] and combining the result with Equation [1]
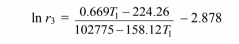
Substituting this into Equation [4] and combining the result with Equation [1]
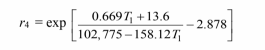
Finally, substituting this into Equation [5] and combining the result with Equation [1]
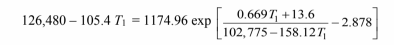
Solving this by trial and error: T1 = 648.15°C
This result can be substituted into the equations above to find the unknown radii

The thickness of the high temperature insulation = r3 – r2 = 6.015 cm
The thickness of the magnesia insulation = r4 – r3 = 6.56 cm
(b) Substituting T1 = 647°C into [1] yields a heat transfer rate of 289 W/m. The overall heat transfer
coefficient based on the pipe outside area must satisfy the following equation
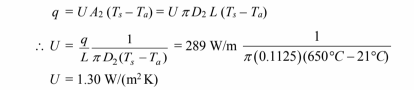
(c) The overall resistance for the insulated pipe is
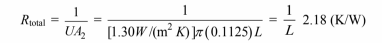
(1) The thermal resistance of the steam side convection is
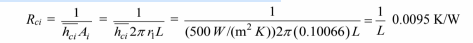
The fraction of the resistance due to steam side convection = 0.0095/3.57 = 0.00.
(2) The thermal resistance of the steel pipe is
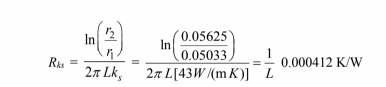
The fraction of the resistance due to the steel pipe = 0.000412/2.18 = 0.00015
(3) The thermal resistance of the magnesia insulation is
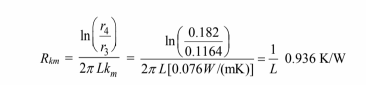
The thermal resistance of the high temperature insulation is
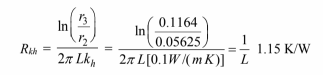
The fraction of the resistance due to the insulation = 2.09/2.18 = 0.96.
(4) The convective thermal resistance on the air side is
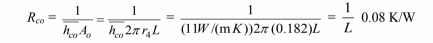
The fraction of the resistance due to air side convection = 0.08/2.18 = 0.04.
(d) The rate of heat transfer is
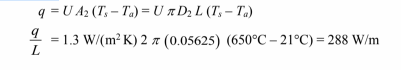
You might also like to view...
The center of a long uniform log is raised to shoulder level while the other end is on the ground. If instead, the end of the log is raised to shoulder level, the work required is
A) half. B) the same. C) twice.
The first to be credited with the idea that light is quantized was
A) Max Planck. B) Albert Einstein. C) both Planck and Einstein at about the same time.
Increased reactant concentration usually leads to an increase in reaction rate, because collisions are
a. more violent only. b. more frequent only. c. both more violent and more frequent. d. none of these
A person with an initial mass of 70 kg climbs a stairway and thereby rises 6.0 m in elevation
By how much does his mass increase by virtue of his increased potential energy? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s)