What is the kinetic energy of a 0.160-kg ball thrown at 40.0 m\/s (90.0 mph)?
Answer: Given that -
m = 0.160 kg
v = 40.0 m/s
Kinetic energy, KE = (1/2)*m*v^2
put the values -
KE = 0.5*0.160*40^2 = 128 Joule.
You might also like to view...
In a heat exchanger, as shown in accompanying figure, air flows over brass tubes of 1.8- cm-ID and 2.1-cm-OD that contain steam. The convection heat-transfer coefficients on the air and steam sides of the tubes are 70 W/(m2 K) and 210 W/(m2 K), respectively. Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger (a) based on the inner tube area, (b) based on the outer tube area.
GIVEN
• Air flow over brass tubes containing steam
• Tube diameters
? Inside (Di) = 1.8 cm = 0.018 m
? Outside (Do) = 2.1 cm = 0.021 m
• Convective heat transfer coefficients
? Air side h c= 70 W/(m2 K)
? Steam side h i= 210 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• The overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger based on
(a) the inner tube area (Ui) and
(b) the outer tube area (Uo)
ASSUMPTIONS
• The heat transfer coefficients are uniform over the transfer surfaces
SKETCH
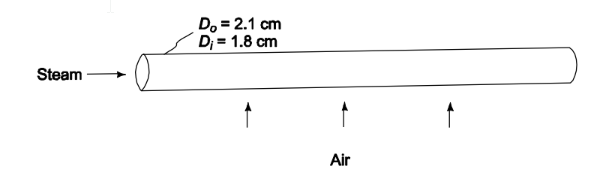
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the thermal conductivity of brass at 20°C (kb) = 111 W/(m K)
An 8000 kg satellite is launched from the surface of the earth, and injected into a circular orbit at an altitude of 100 km above the surface of the earth. The kinetic energy of the satellite in the circular orbit is 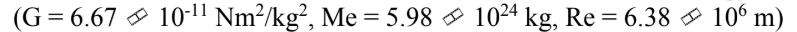
A. 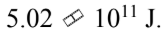
B. 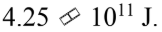
C. 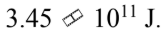
D. 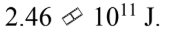
E. 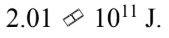
A 2000-kg sailboat experiences an eastward force of 3000 N by the ocean tide and a wind force against its sails of magnitude 6000 N directed toward the northwest (45° N of W). What is the magnitude and direction of the resultant acceleration?
What will be an ideal response?
A very dense 1500-kg point mass (A) and a dense 1200-kg point mass (B) are held in place 1.00 m apart on a frictionless table
A third point mass is placed between the other two at a point that is 20.0 cm from B along the line connecting A and B. When the third mass is suddenly released, find the magnitude and direction (toward A or toward B) of its initial acceleration. (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ? m2/kg2)