A perfectly competitive firm is a price taker because
A. It has market power.
B. Its products are differentiated.
C. Market supply is upward-sloping.
D. The price of the product is determined by many buyers and sellers.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. The Engel curve contains information that is not found in the indifference curve diagram. 2. The Law of demand can only be violated if a good is inferior. 3. All Giffen goods must be inferior goods, but not all inferior goods are Giffen goods. 4. In a two-good world, one good-but not both-can be inferior. 5. An inferior good is one for which the substitution effect is relatively large.
Assume that a hurricane in Brazil destroys half of the coffee crop. Considering that Brazil is a major coffee producing country, consumers expect the price of coffee to increase in the near future. How does this reflect on the demand for coffee?
a. There is a movement upward along the demand curve for coffee. b. The demand curve for coffee shifts inward. c. The demand curve for coffee shifts outward. d. There is a movement downward along the demand curve for coffee. e. The demand for coffee declines.
The competitive price-taker model is usually used to illustrate the competitive process. If firms cannot choose their price, where is the competition?
Assuming the inner curve is the United States' current production possibilities frontier, which of the following points would eventually lead to the greatest level of economic growth?
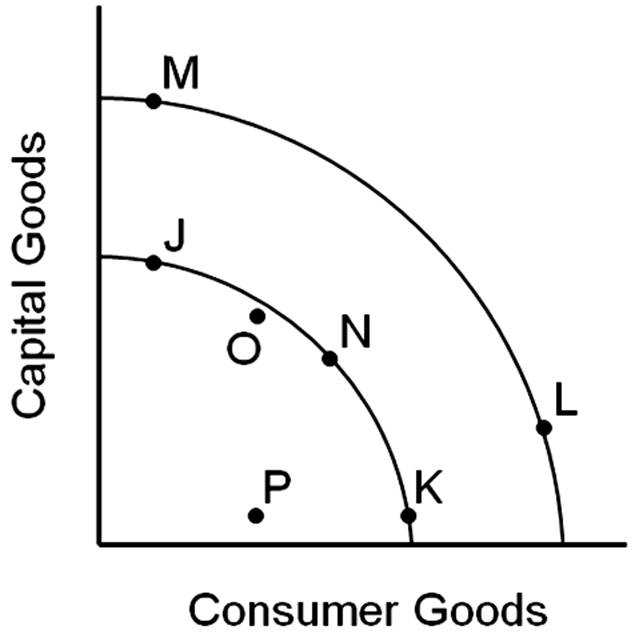
A. Point J
B. Point N
C. Point K
D. Point P