A 2.5-cm-diameter cylindrical refractory crucible for melting lead is to be built for thermocouple calibration. An electrical heater immersed in the metal is shut off at some temperature above the melting point. The fusion-cooling curve is obtained by observing the thermocouple emf as a function of time. Neglecting heat losses through the wall of the crucible, estimate the cooling rate (W) for the molten lead surface (melting point 327.3°C, surface emissivity 0.8) if the crucible depth above the lead surface is (a) 2.5 cm, (b) 17 cm. Assume that the emissivity of the refractory surface is unity and the surroundings are at 21°C, (c) Noting that the crucible would hold about 0.09 kg of lead for which the heat of fusion is 23,260 J/kg, comment on the suitability of the crucible for the
purpose intended.
GIVEN
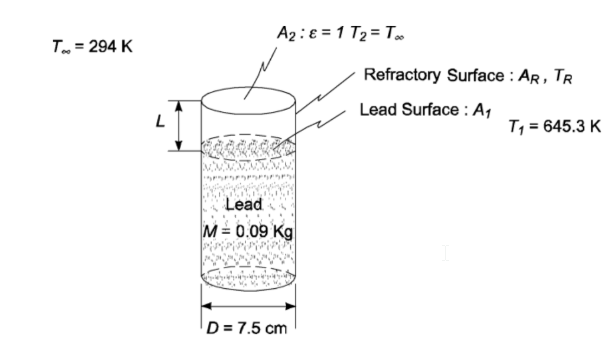
A cylindrical refractory crucible filled with molten lead
Cylinder diameter (D) = 2.5 cm
Melting point of lead (T1) = 327.2°C = 600.3 K
Surface emissivity of lead (?1) = 0.8
Mass of lead in crucible (m) = 0.09
Heat of fusion of lead (hfg) = 23,260 J/kg
FIND
The cooling rate (q) if the crucible depth above the lead surface (L) is
(a) 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
(b) 17 cm = 0.17 m
(c) Comment on the suitability of the crucible for thermocouple calibration
ASSUMPTIONS
Heat loss through the wall of the crucible is negligible
The emissivity of the refractory surface (crucible wall above the lead) is unity (?2 =1)
The surroundings behave as a blackbody enclosure
The temperature of the refractory surface is uniform at TR
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant
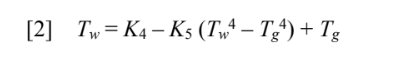
for air at the film temperature of
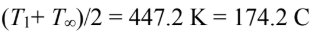
Thermal expansion coefficient
Thermal conductivity
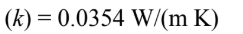
Kinematic viscosity
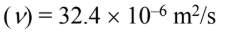
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
The total cooling rate is the sum of natural convection and radiation
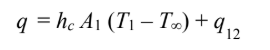
where q12 is the radiative heat transfer between the two surfaces connected by a refractory wall and is
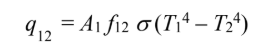
where A1 f12 (Note that ?2 = 1.0 and A2 = A1)
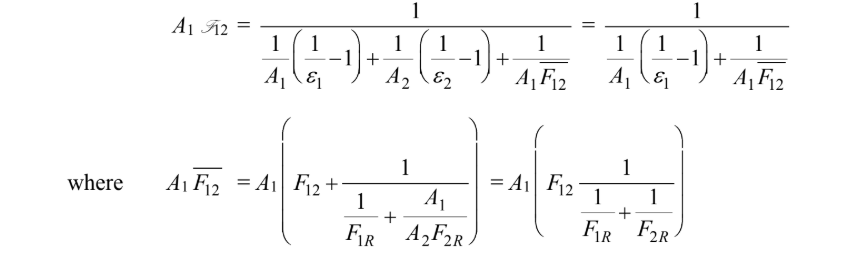
The shape factor by letting a = b = D/s and
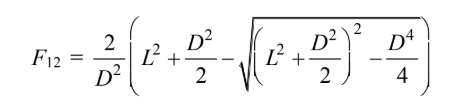
The shape factor by letting a = b = D/s and
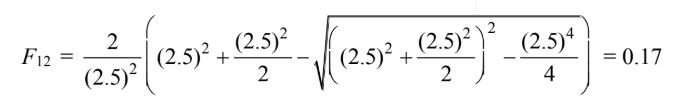
For Case (a)
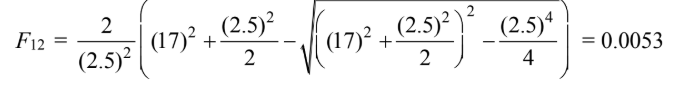
For Case (b)
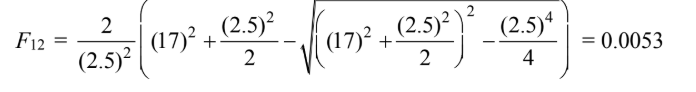
By symmetry
F21 = F12
The shape factors from a given surface must sum to unity
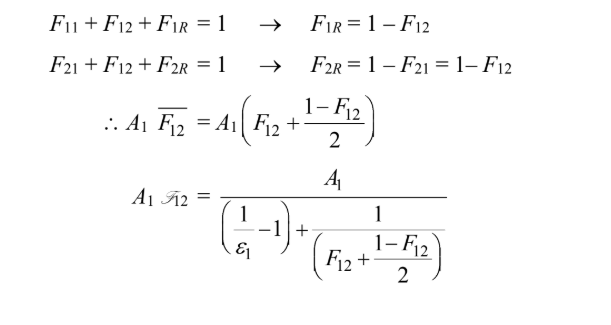
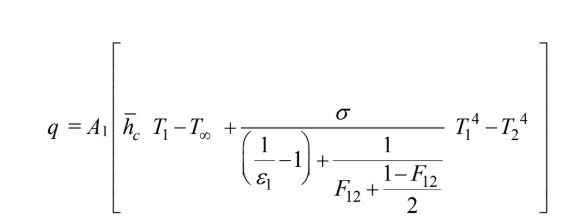
The heat transfer coefficient, hc, can be calculated

Although this is slightly below its lower Rayleigh number range, Equation (5.15) will be used to estimate the Nusselt number

(a)
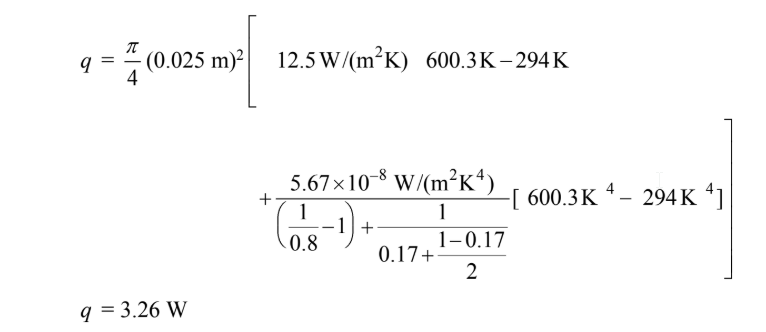
b
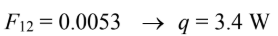
(c) The time required for the lead to solidify at the cooling rate (q) of 3.62 W is given by
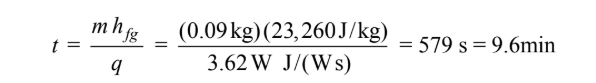
The technician would have about 9.6 minutes to do the calibration. This should be enough time to accomplish the task.
You might also like to view...
Mass on a Spring: A 0.30-kg block of wood is suspended on a spring. In equilibrium the wood stretches the spring 2.0 cm downward. The wood is then pulled an additional distance of 1.0 cm down and released from rest.(a) How long does it take the wood to make 3 complete cycles of vibration?(b) How much total mechanical energy does this system contain if we choose the total potential energy (elastic and gravitational) to be zero at the equilibrium position of the hanging block?
What will be an ideal response?
Regarding the validity of the law of conservation of energy,
A) it is valid for any situation in which Newtonian physics is valid, but is often incorrect outside of that range. B) it is valid in all situations except those situations involving heat. C) this law is a consequence of Newtonian physics, and so this law is valid in every known situation because Newtonian physics is valid in every known situation. D) it is valid in every known situation--including those situations in which Newtonian physics is not valid.
The splitting of a large nucleus into two smaller nuclei upon absorbing a neutron is nuclear fusion
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Gamma radiation is used to kill harmful bacteria in food
Indicate whether the statement is true or false