List and give examples of the five pitfalls to economic thinking
Please provide the best answer for the statement.
First, bias and preconceptions can cloud economic thinking. An example would be the belief that “the only reason people are unemployed is that they are too lazy to work.” Second, economic terminology in the popular press can be slanted or emotionally loaded. Examples of loaded or slanted terms are “corporate welfare,” “gouging the consumer,” and “exorbitant salaries.” Third, there is the problem of definition of terms. For example, the term “capital” may refer either to “capital goods” or “financial capital.” Fourth, you make a mistake when you assume that what is true for the individual or part of a group is also true for the group as a whole. For example, if an individual stands up to see better at a football game, the individual is better off, but if all the fans stand up to see better, the group is not better off. Fifth, there are two causation fallacies. You might conclude that one event causes the other simply because one preceded the other (the after this, therefore because of this causation): “I washed my car, therefore it rained.” You might also confuse correlation with causation: “incomes rose and the crime rate fell, thus higher incomes reduce the crime rate.”
You might also like to view...
A major problem with using the egalitarian principle to distribute income is that
A) it would eliminate the incentives that rewards provide in an economic system. B) it is difficult to know when an equal distribution of income has been achieved. C) it would not be fair to the wealthy. D) there exist no mechanisms to carry out such a scheme.
If the demand curve increases while the supply curve remains unchanged, the equilibrium price would increase
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
________ states that when an established domestic industry is in jeopardy of being displaced by lower-priced imports, then there could be a rationale for temporary import restrictions
a. The infant industry argument b. The antidumping argument c. The jobs and income argument d. The declining industry argument
What is the value of I? – I?
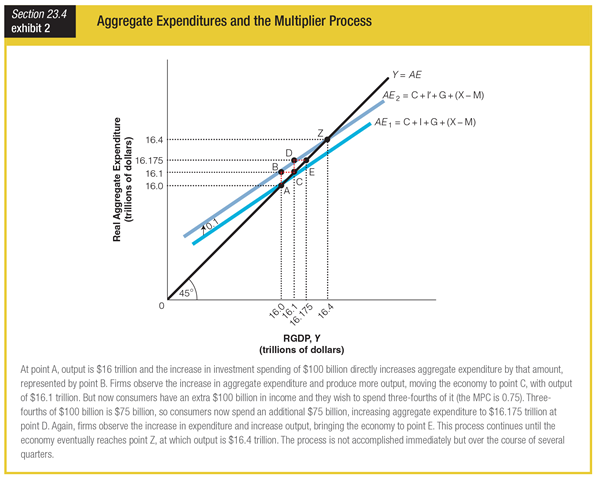
a. $0
b. $100 billion
c. $175 billion
d. $400 billion