Refer to Figure 20.3 below. Suppose the equation that equates excess burden to the tax rate can be written as EB = t 2 , where EB is excess burden and t is the tax rate.
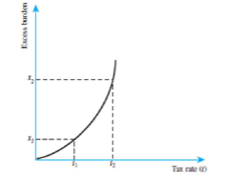
(A) Suppose the tax rate t is initially 12 percent. How much excess burden is generated?
(B) If the tax rate doubles to 24 percent, what happens to excess burden?
(A) When the tax rate is 12 percent, EB is 0.12 2 = 0.0144.
(B) When the tax rate doubles, EB is 0.24 2 = 0.0576, which is more than double.
You might also like to view...
Out of a set of feasible alternatives, an optimizer should choose the alternative with the:
A) highest net benefit. B) highest opportunity cost. C) lowest total cost, regardless of benefit. D) highest total benefit, regardless of cost.
The concept of market conduct includes such things as ____
a. pricing behavior of the firm or group of firms b. product policy of the firm or group of firms c. the degree of seller and buyer concentration in the market d. a and b only e. a, b, and c
We would expect the interest rate on Bond A to be higher than the interest rate on Bond B if the two bonds have identical characteristics except that
a. the credit risk associated with Bond A is lower than the credit risk associated with Bond B. b. Bond A was issued by the city of Philadelphia and Bond B was issued by Red Hat Corporation. c. Bond A has a term of 20 years and Bond B has a term of 2 years. d. All of the above are correct.
Which one of the following is NOT money?
A. Gold B. A dime C. A demand deposit D. A NOW account