A homeowner wants to replace an electric hot-water heater. There are two models in the store. The inexpensive model costs $280 and has no insulation between the inner and outer walls. Due to natural convection, the space between the inner and outer walls has an effective conductivity of 3 times that of air. The more expensive model costs $310 and has fiberglass insulation in the gap between the walls. Both models are 3.0 m tall and have a cylindrical shape with an inner wall diameter of 0.60 m and a 5 cm gap. The surrounding air is at 25°C, and the convective heat transfer coefficient on the outside is 15 W/(m2 K). The hot water inside the tank results in an inside wall temperature of 60°C. If energy costs 6 cents per kilowatt-hour, estimate how long it will take to pay back the extra
investment in the more expensive hot-water heater. State your assumptions.
GIVEN

FIND
- The time it will take to pay back the extra investment in the more expensive hot-water heater
ASSUMPTIONS
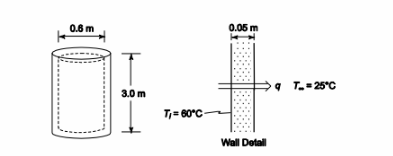
- Since the diameter is large compared to the wall thickness, one-dimensional heat transfer is
assumed
- To simplify the analysis, we will assume there is no water drawn from the heater, therefore the
inside wall is always at 60°C
- Steady state conditions prevail
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
fiberglass (ki) = 0.035 W/(m K) at 20°C
dry air (ka) = 0.0279 W/(m K) at 60°C
The areas of the inner and outer walls are
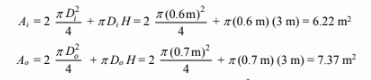
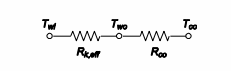
The average area for the air or insulation between the walls (Aa) = 6.8 m2.The thermal circuit for water
heater #1 is
The rate of heat loss for water heater #1 is
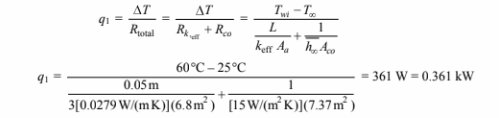
Therefore the cost to operate water heater #1 is
Cost1 = q1 (energy cost) = 0.361 kW ($0.06/kWh) (24 h/day) = $0.52/day
The thermal circuit for water heater #2 is
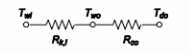
The rate of heat loss from water heater #2 is
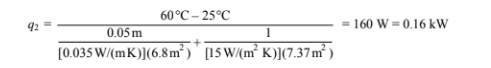
Therefore the cost of operating water heater #2 is
Cost2 = q2 (energy cost) = 0.16 kW ($0.06/kWh) (24 h/day) = $0.23/day
The time to pay back the additional investment is the additional investment divided by the difference
in operating costs
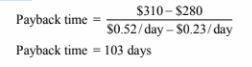
You might also like to view...
You observe a full Moon rising at sunset. What will you see at midnight?
A) a full Moon high in the sky B) a first quarter Moon C) a waning gibbous Moon D) a third quarter Moon
A 5.0-kg mass sits on the floor of an elevator that has a downward acceleration of 1.0 m/s2. On top of the 5.0-kg mass is an object of unknown mass. The force of the elevator on the 5.0-kg mass is 80 N up. Determine the unknown mass.
A. 3.3 kg B. 2.4 kg C. 1.6 kg D. 4.1 kg E. 5.0 kg
What is the binding energy of the 4He nucleus?
A) 14.15 MeV B) 28.3 MeV C) 7.80 MeV D) 10.77 MeV E) 20.36 MeV
What is the inductive reactance of a 20-mH inductor at a frequency of 60 Hz?
A) 7.5 ? B) 0.13 ? C) 1.2 ? D) 1.2 m? E) 7.5 m?