Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.11 below to answer the question(s) that follow.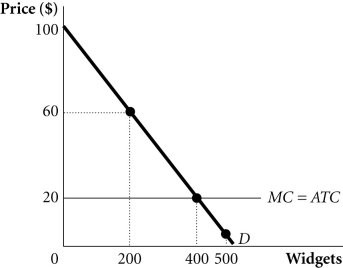 Figure 13.11Refer to Figure 13.11. Suppose a monopolist faces the demand and costs in the figure and is able to perfectly price discriminate. The monopolist will ________ $16,000.
Figure 13.11Refer to Figure 13.11. Suppose a monopolist faces the demand and costs in the figure and is able to perfectly price discriminate. The monopolist will ________ $16,000.
A. earn a profit of
B. have total costs equal to
C. have total revenues equal to
D. lose
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
In one year in the country of Countem, workers earned $4150, proprietor's income was $392, rental income was $20, corporate profits were $683,
net interest was $228, taxes on production and imports were $329, business current transfer payments were $12, the current surplus of government enterprises was $3, statistical discrepancy was $28, consumption of fixed capital was $882, factor income received from the rest of the world was $331, and payments of factor income to the rest of the world was $623. Based on these data, compute national income, net national product, gross national product, and gross domestic product.
In the new Keynesian model, the ultimate effect on output of an anticipated aggregate demand shock is ________
A) less than if that event was unanticipated B) greater than if that event was unanticipated C) the same as would develop if that event had never occurred D) dependent on whether or not that event is temporary or permanent
Because market price remains constant as a perfectly competitive firm expands output, each firm faces
a. a downward-sloping demand curve b. a horizontal demand curve c. constant returns to scale d. constant costs e. diminishing marginal revenue
Figure 10-15
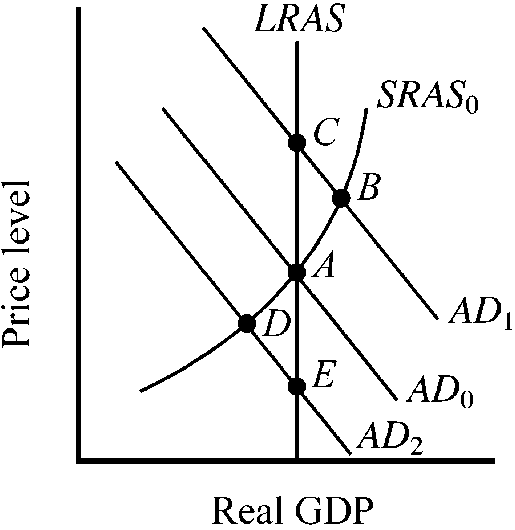
The economy's short-run (SRAS ) and long-run (LRAS) aggregate supply curves are shown in , along with three alternative aggregate demand curves and the accompanying equilibrium points. At which point will resource prices naturally tend to increase?
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
D