The airplane you are riding suddenly depressurizes at 10,000 feet in the air. This causes the PO2 of the airplane's air to drastically decrease. You pass out before you can put on your oxygen mask. After a few seconds, the PO2 in your alveoli rapidly drops to 60 mmHg instead of the normal 104 mmHg. How will this affect blood gas concentrations?
A. Blood PO2 will become low and much less oxygen will be delivered to tissues until cabin pressure returns.
B. PO2 in the alveoli will be so low that oxygen will diffuse from hemoglobin into the alveoli, where it is exhaled. This causes blood oxygen concentrations to drop throughout the body.
C. PO2 in the alveoli will be too low for gas exchange to even occur, so tissues will receive no oxygen during the depressurization event.
D. Blood PCO2 will increase because the air contains less oxygen.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Muscarinic ACh receptors are found in all of the following locations EXCEPT _____
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Which endocrine gland secretions do not appear to decrease as one ages?
A. Melatonin B. Thyroid hormones C. Parathyroid hormone D. Growth hormone
The normal range of arterial blood pH is ________.
A. 7.35-7.45 B. 7.15-7.25 C. 6.95-7.05 D. 6.50-7.50
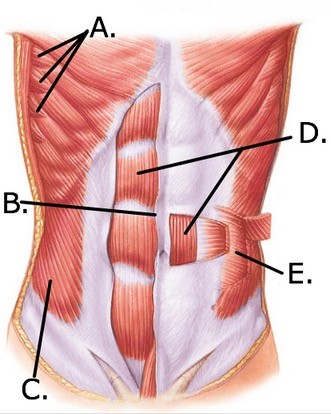 The figure illustrates muscles of the thorax and abdomen. Which structure is indicated by "B"?
The figure illustrates muscles of the thorax and abdomen. Which structure is indicated by "B"?
A. Serratus anterior B. External oblique C. Internal oblique D. Rectus abdominis E. Linea alba