Using a graph, explain why the law of supply holds for a competitive firm.
What will be an ideal response?
According to the law of supply, when the market price increases, the profit-maximizing sales quantity for a price-taking firm never decreases. Figure 9.7 illustrates why a price-taking firm never decreases its supply when the market price rises.
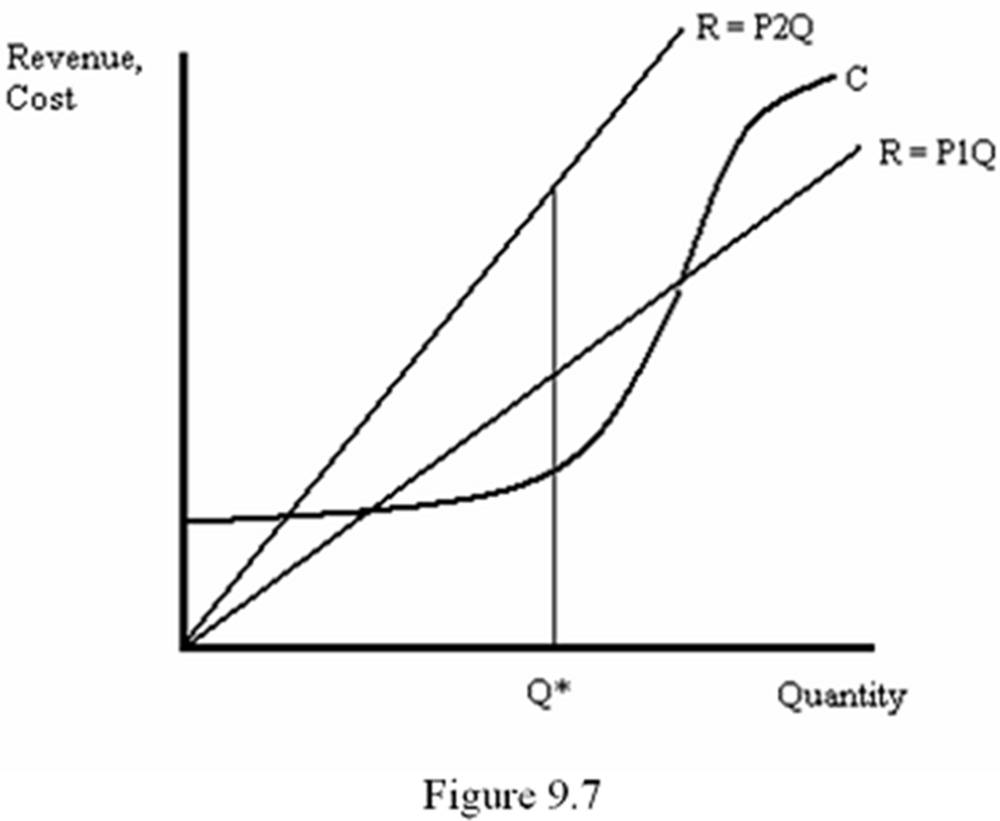
Quantity Q* maximizes the distance between the firm's revenue and cost curves when the product price is P1. When price rises to P2, revenue rises more at Q* than it does at smaller quantities. Since Q* was better than any smaller quantity when price was P1, it will be better than any quantity when price rises to P2.
You might also like to view...
Utilitarianism is a principle whose goal is ________
A) the greatest happiness for the greatest number B) the greatest pay for the greatest number C) equal pay for equal work D) equal happiness for all workers
According to the profit-maximization goal, the firm should attempt to maximize short-run profits since there is too much uncertainty associated with long-run profits
a. true b. false
One effect of the lemons problem in the used car market is that
a. the market is efficient b. without reliable information, lemons become increasingly common c. no good cars are offered on the market d. no lemons are offered on the market e. good cars sell at more than their market value
Assume that the central bank lowers the discount to increase the nation's monetary base. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the quantity of real loanable funds per time period and real GDP in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? State your answer after the macroeconomic system returns to complete equilibrium
a. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period falls and real GDP falls. b. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises and real GDP rises. c. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises and real GDP remains the same. d. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period and real GDP remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.