Energy Conservation With Nonconservative Forces: A heavy sled and a light sled, both moving horizontally with the same kinetic energy, suddenly slide onto a rough patch of snow and eventually come to a stop. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the sleds and the rough snow is the same for both of them. Which of the following statements about these sleds are correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A. Both sleds will slide the same distance on the rough snow before stopping.
B. The heavy sled will slide farther on the rough snow than the light sled.
C. The light sled will slide farther on the rough snow than the heavy sled.
D. On the rough snow, the change in kinetic energy will be the same for both sleds.
E. The friction from the snow will do the same amount of work on both sleds.
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
The planet in our solar system with the highest average surface temperature is
A) Venus B) Mercury C) Earth D) Neptune
A 5-kg piece of lead (specific heat 0.03 cal/g/°C) having a temperature of 80°C is added to 500 g of water having a temperature of 20°C. What is the final equilibrium temperature (in °C) of the system?
a. 79 b. 26 c. 54 d. 34 e. 20
Slanting Surfaces Without Friction: A 15-kg block is on a frictionless ramp that is inclined at 20° above the horizontal. It is connected by a very light string over an ideal pulley at the top edge of the ramp to a hanging 19-kg block, as shown in the figure. The string pulls on the 15-kg block parallel to the surface of the ramp. Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the 19-kg block after the system is gently released?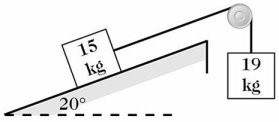
A. 4.0 m/s2 B. 3.8 m/s2 C. 4.2 m/s2 D. 4.5 m/s2
On the H-R diagram, the Sun lies
A) about the middle of the main sequence. B) at the top left. C) at the bottom right. D) at the bottom left. E) at the top right.