According to the classical economists, an economy producing $15 trillion in goods and services
A) may be producing too much since the needs of people may not be this great.
B) could experience a permanent glut if no one has estimated the demand for goods and services in the economy.
C) simultaneously generates the income necessary to purchase $15 trillion in goods and services.
D) is supplying $15 trillion in goods and services, but could be demanding more or less than $15 trillion in goods and services for a very long period of time.
C
You might also like to view...
What happens as the result of a shortage?
A) There is downward pressure on prices. B) There is upward pressure on prices. C) Consumers begin to view the good as an inferior good because they have a hard time finding it. D) Supply of the good decreases.
A decrease in the price of a substitute shifts the demand curve to the _______
a. right b. left c. it does not change the demand curve d. none of the above
According to the graph shown, if the market price decreases (all else staying the same):
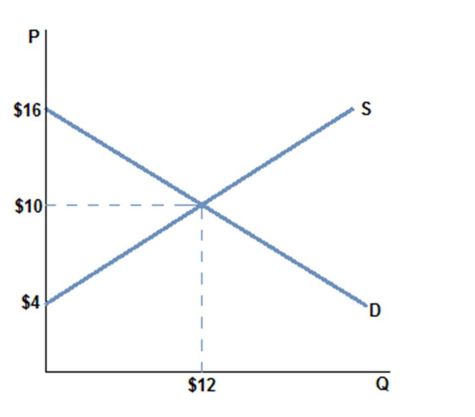
A. producer surplus would increase.
B. producer surplus would decrease.
C. total surplus would increase.
D. quantity would increase.
Graphically the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply line determines:
A. long-run equilibrium. B. exogenous spending. C. potential output. D. short-run equilibrium.