During the course of the twentieth century, the average workweek in the United States has gotten shorter and Americans have enjoyed greater amounts of leisure time. How has this development affected potential GDP and labor productivity?
What will be an ideal response?
Decreasing the length of the workweek, other things being equal, should decrease potential GDP. As Americans enjoy longer leisure hours and shorter work hours, the goods and services such work would produce will decrease. The United States could increase the amount of potential GDP that the economy produces if Americans would decide to work longer hours or more days per week. This would not necessarily mean that Americans would be better off since, obviously, the benefits and pleasures of some leisure time would be foregone. The main reason that the amount of final goods and services enjoyed by Americans has not decreased even with shorter work hours is that labor productivity has increased. Since labor productivity measures output per hour worked, it does not automatically decrease as the total number of hours worked decreases. In fact, during the twentieth century, labor productivity in the United States has increased significantly. This has occurred mainly due to technical progress and the increasing education and skill levels of the American worker.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following clearly restricts competition?
A) A government policy restricting entry into the market B) A government policy that reduces tariffs on foreign imports C) A business sets price below cost. D) A business sets price above cost. E) Any business pricing scheme that successfully draws customers away from its rivals
Which of the following is an accurate example of what an individual demand curve shows?
a. Dave’s demand for blue jeans will increase as the price of blue jeans drops. b. As the overall price of goods in the United States increases, the demand for goods decreases. c. When the demand for KDF sneakers decreased, the company tried a new design. d. Chicago’s legal firms raised their fees, causing the number of law firms to increase.
Suppose that on a typical day, a restaurant owner usually sells 18 club sandwiches. However, after lowering the price of a club sandwich from $6.75 to $5.95, the owner discovered that sales increased to 23 sandwiches per day. Based on this information, the restaurant owner calculated that the demand elasticity for club sandwiches was approximately:
a. -0.05 b. -0.52 c. -1.94 d. -20.2
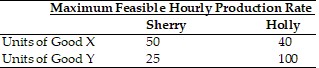 According to the above table, which assumes that opportunity costs of producing goods X and Y are constant, which of the following statements is TRUE?
According to the above table, which assumes that opportunity costs of producing goods X and Y are constant, which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. Holly will be willing to produce only good X and trade units of that good to Sherry as long as she receives less than 2.5 units of good Y in exchange. B. Holly will be willing to produce only good Y and trade units of that good to Sherry as long as she receives less than 0.4 unit of good X in exchange. C. Sherry will be willing to produce only good Y and trade units of that good to Holly as long has she receives less than 2 units of good X from her in exchange. D. Sherry will be willing to produce only good X and trade units of that good to Holly as long as she receives more than 0.5 units of good Y from her in exchange.