In the diagram, the economy's long-run aggregate supply curve is shown by line:
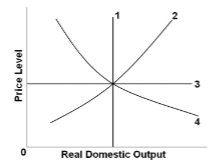
A. 1.
B. 2.
C. 3.
D. 4.
A. 1.
You might also like to view...
In a typical college classroom without a seating chart, dozens of students nevertheless occupy classroom seats with a minimum of confusion and disorder. Economics explains the orderly process of seat selection by assuming students
A) engage in entirely random decisions, from which only divine intervention can generate order in the classroom. B) follow a simple, perhaps even unwritten, rule, such as "seats belong to the person who first occupies them." C) know all the consequences of their actions, and thus purposefully create an orderly classroom seating assignment even if the professor doesn't require one. D) trick question: economics cannot deduce any sensible scientific claims about the behavior of college students.
The difference between the marginal social cost and the marginal private cost equals the
A) cost of producing an additional unit of a good. B) marginal external benefit. C) marginal external cost. D) marginal private benefit.
"Insider trading" laws are meant to prevent
A) the executives of a corporation from holding a majority of its outstanding shares. B) buying or selling shares based on information not available to the public. C) foreign investors from gaining controlling interest in U.S. corporations. D) the issuing of bonds for the purpose of buying stock.
The mechanism of supply and demand is
a. a fundamental tool in both microeconomics and macroeconomics. b. the only real "law" of economics. c. a fundamental tool only in microeconomics. d. a fundamental tool only in macroeconomics.