Explain how the outcome of the Cournot model is achieved
What will be an ideal response?
The Cournot model begins with a new firm producing nothing and the existing firm producing the entire amount of industry output. When the new firm begins operating, it assumes that the existing firm will continue to act as a monopolist. This means that the demand curve for the new firm is everything on the demand curve below the price charged by the existing firm. Once the new firm begins producing, the existing firm finds that its demand is lower. When it begins to make output decisions, it believes that the new firm's output will remain constant and therefore produces a lower output. This will change the amount that the new firm wants to produce which will change the amount that the existing firm wants to produce. The adjustments continue until the two firms split the market and charge the same price.
You might also like to view...
If someone gives you a free ticket to the movies, then there is no opportunity cost involved with going to the movies
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Welfare reforms enacted in 1996 put more pressure on welfare recipients to look for work. The new law mandated cutting off benefits after a certain length of time. Which of the following is likely to occur as a result of this provision?
A. the natural rate of unemployment and the unemployment rate are likely to increase. B. the natural rate of unemployment is likely to decrease, but the unemployment rate is likely to increase. C. the natural rate of unemployment is not affected, but the unemployment rate is likely to increase. D. the natural rate of unemployment is not affected, but the unemployment rate is likely to fall.
If sugar and Nutrasweet are substitutes, then we can be certain that an increase in the price of sugar will lead to an increase in the consumption of:
A. sugar only. B. Nutrasweet only. C. sugar and Nutrasweet. D. None of the statements is correct.
Refer to the information provided in Table 33.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 33.1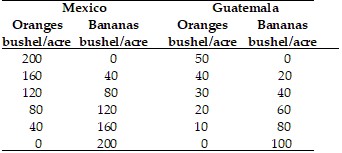 Refer to Table 33.1. The opportunity cost of producing a bushel of oranges in Mexico is
Refer to Table 33.1. The opportunity cost of producing a bushel of oranges in Mexico is
A. four times as much as that in Guatemala. B. twice as much as that in Guatemala. C. half as much as that in Guatemala. D. the same as that in Guatemala.