Two identical small conducting spheres are separated by 0.60 m. The spheres carry different amounts of charge and each sphere experiences an attractive electric force of 10.8N
The total charge on the two spheres is -24 ?C. The two spheres are now connected by a slender conducting wire, which is then removed. The electric force on each sphere is closest to
A) 5.4 N, repulsive.
B) zero.
C) 3.6 N, attractive.
D) 5.4 N, attractive.
E) 3.6 N, repulsive.
E
You might also like to view...
X-rays with an energy of 400 keV undergo Compton scattering from a target. The scattered rays are deflected at an angle of 38° relative to the direction of the incident rays.What is the kinetic energy of the recoiling electrons?
a. 56.9 J b. 51.5 J c. 34.3 J d. 13.7 J
The orbital angular momentum quantum number ? can have any integer value ranging from
A) 0 to n. B) 0 to (n-1). C) 1 to n. D) 1 to (n+1). E) -n to n.
Hydrogen, nitrogen, and chlorine are among the elements that occur as molecules made up of ______________ atoms
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Consider fully developed laminar flow of a fluid inside a wide rectangular duct with both the upper and lower surface at uniform surface temperature, as schematically shown in the figure below. The effect of the two sides of the duct is neglected (W>> H), and at a location far from the entrance the velocity distribution is assumed to be uniform, u(x) = Cu whereas the temperature distribution has a parabolic profile given by T(x)= Ts + CT (1 –(2x/H)2). From the given velocity and temperature distributions, calculate the Nusselt number, which is given by its definition as where Tb is the average bulk temperature of the flowing fluid at the specified location, and k is the thermal conductivity of the fluid.
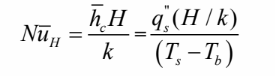
GIVEN
Fully developed laminar flow of fluid inside rectangular duct
Uniform upper and lower surface temperature
Uniform velocity distribution u(x) = Cu
Parabolic temperature distribution T(x)= Ts + CT (1 –(2x/H)2
FIND
Nusselt number
SKETCH